New clues to understanding HIV nonprogressors: low cholesterol blocks HIV trans infection
- PMID: 24917601
- PMCID: PMC4056555
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01396-14
New clues to understanding HIV nonprogressors: low cholesterol blocks HIV trans infection
Abstract
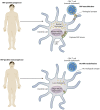
A small percentage of HIV-infected subjects (2 to 15%) are able to control disease progression for many years without antiretroviral therapy. Years of intense studies of virologic and immunologic mechanisms of disease control in such individuals yielded a number of possible host genes that could be responsible for the preservation of immune functions, from immune surveillance genes, chemokines, or their receptors to anti-HIV restriction factors. A recent mBio paper by Rappocciolo et al. (G. Rappocciolo, M. Jais, P. Piazza, T. A. Reinhart, S. J. Berendam, L. Garcia-Exposito, P. Gupta, and C. R. Rinaldo, mBio 5:e01031-13, 2014) describes another potential factor controlling disease progression: cholesterol levels in antigen-presenting cells. In this commentary, we provide a brief background of the role of cholesterol in HIV infection, discuss the results of the study by Rappocciolo et al., and present the implications of their findings.
Copyright © 2014 Prasad and Bukrinsky.
Figures
Comment on
-
Alterations in cholesterol metabolism restrict HIV-1 trans infection in nonprogressors.mBio. 2014 Apr 29;5(3):e01031-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01031-13. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24781743 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

