SIRT1 ameliorates age-related senescence of mesenchymal stem cells via modulating telomere shelterin
- PMID: 24917814
- PMCID: PMC4042159
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00103
SIRT1 ameliorates age-related senescence of mesenchymal stem cells via modulating telomere shelterin
Abstract
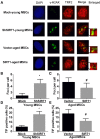
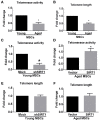
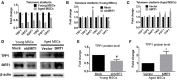
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) senescence is an age-related process that impairs the capacity for tissue repair and compromises the clinical use of autologous MSCs for tissue regeneration. Here, we describe the effects of SIRT1, a NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase, on age-related MSCs senescence. Knockdown of SIRT1 in young MSCs induced cellular senescence and inhibited cell proliferation whereas overexpression of SIRT1 in aged MSCs reversed the senescence phenotype and stimulated cell proliferation. These results suggest that SIRT1 plays a key role in modulating age-induced MSCs senescence. Aging-related proteins, P16 and P21 may be downstream effectors of the SIRT1-mediated anti-aging effects. SIRT1 protected MSCs from age-related DNA damage, induced telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) expression and enhanced telomerase activity but did not affect telomere length. SIRT1 positively regulated the expression of tripeptidyl peptidase 1 (TPP1), a component of the shelterin pathway that protects chromosome ends from DNA damage. Together, the results demonstrate that SIRT1 quenches age-related MSCs senescence by mechanisms that include enhanced TPP1 expression, increased telomerase activity and reduced DNA damage.
Keywords: SIRT1; TPP1; aging; mesenchymal stem cells; senescence; shelterin; telomerase.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PBX1-SIRT1 Positive Feedback Loop Attenuates ROS-Mediated HF-MSC Senescence and Apoptosis.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Feb;19(2):443-454. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10425-w. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 35962175 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase mediates the senescence of mesenchymal stem cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Sep;36(3):857-64. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2284. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26178664
-
Cordycepin Enhances SIRT1 Expression and Maintains Stemness of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.In Vivo. 2023 Mar-Apr;37(2):596-610. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13118. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 36881089 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue formation and tissue engineering through host cell recruitment or a potential injectable cell-based biocomposite with replicative potential: Molecular mechanisms controlling cellular senescence and the involvement of controlled transient telomerase activation therapies.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 Dec;103(12):3993-4023. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35515. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015. PMID: 26034007 Review.
-
Impact of circadian disruption on health; SIRT1 and Telomeres.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Dec;96:102993. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102993. Epub 2020 Sep 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33038659 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of telomere-binding modulators in pluripotent stem cells.Protein Cell. 2020 Jan;11(1):60-70. doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-0651-y. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Protein Cell. 2020. PMID: 31350723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uterine-specific SIRT1 deficiency confers premature uterine aging and impairs invasion and spacing of blastocyst, and stromal cell decidualization, in mice.Mol Hum Reprod. 2022 Jun 30;28(7):gaac016. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaac016. Mol Hum Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35536234 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Genomic Hallmarks of Aging-The Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15468. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015468. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventing MSC aging and enhancing immunomodulation: Novel strategies for cell-based therapies.Regen Ther. 2025 May 5;29:517-539. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.04.014. eCollection 2025 Jun. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 40453699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Landscape of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Senescence Mechanisms and Implications on Therapeutic Strategies.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jul 17;7(8):2306-2325. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00284. eCollection 2024 Aug 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39144566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

