Increased risk of ischemic stroke in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a 9-year follow-up nationwide population study in taiwan
- PMID: 24917815
- PMCID: PMC4040439
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00108
Increased risk of ischemic stroke in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a 9-year follow-up nationwide population study in taiwan
Abstract
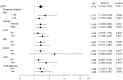
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a common form of vertigo and is characterized by episodic dizziness related to changes in head position relative to gravity. BPPV symptoms can be similar to those of central nervous system vascular diseases. The association between BPPV and ischemic stroke has not yet been investigated. The study cohort consisted of patients who were diagnosed with BPPV at least twice in the previous year as an outpatient or for whom BPPV was the primary diagnosis as an inpatient (n = 4104). An age- and gender-matched sample that excluded patients with a diagnosis of any form of vertigo was selected as the comparison cohort (n = 8397). All cases were followed up from January 1, 2000, to December 31, 2008. The demographic characteristics, medical comorbidities, and use of medications in both groups were investigated using chi-square tests. A stratified analysis of stroke risk factors was performed to determine the hazard ratios of BPPV. During the 9-year follow-up period, 185 of the 4104 (4.5%) subjects with BPPV and 240 of the 8379 (2.9%) subjects without BPPV developed ischemic strokes. The crude hazard ratio of BPPV for developing ischemic strokes was 1.708. After adjusting for stroke risk factors, the risk of developing ischemic strokes in BPPV subjects was 1.415-fold higher than the risk among those without BPPV (confidence interval: 1.162-1.732, p = 0.001). After a subgroup analysis stratified according to stroke risk factors, BPPV remained independently associated with a higher risk of developing future ischemic stroke. We conclude that BPPV is independently associated with a risk of subsequent ischemic stroke. More aggressive control of modifiable risk factors for ischemic strokes should be conducted in patients with BPPV.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; dizziness; risk factors; stroke; vertigo.
Figures
References
-
- Baloh R. W. (1992). Dizziness in older people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 40, 713–721 - PubMed
-
- Baloh R. W., Sloane P. D., Honrubia V. (1989). Quantitative vestibular function testing in elderly patients with dizziness. Ear Nose Throat J. 68, 935–939 - PubMed
-
- Bárány E. (1920). Diagnose yon krankheitserscheinungen im bereiche des otolithenapparates. Acta Otolaryngol. 2, 434–43710.3109/00016482009123103 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources