Effect of contraction intensity on sympathetic nerve activity to active human skeletal muscle
- PMID: 24917823
- PMCID: PMC4042086
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00194
Effect of contraction intensity on sympathetic nerve activity to active human skeletal muscle
Abstract
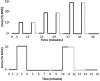
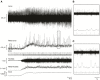
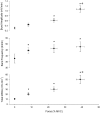
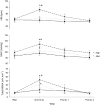
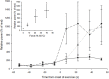
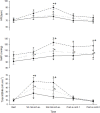
The effect of contraction intensity on muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) to active human limbs has not been established. To address this, MSNA was recorded from the left peroneal nerve during and after dorsiflexion contractions sustained for 2 min by the left leg at ~10, 25, and 40% MVC. To explore the involvement of the muscle metaboreflex, limb ischemia was imposed midway during three additional contractions and maintained during recovery. Compared with total MSNA at rest (11.5 ± 4.1 mv(.)min(-1)), MSNA in the active leg increased significantly at the low (21.9 ± 13.6 mv(.)min(-1)), medium (30.5 ± 20.8 mv(.)min(-1)), and high (50.0 ± 24.5 mv(.)min(-1)) intensities. This intensity-dependent effect was more strongly associated with increases in MSNA burst amplitude than burst frequency. Total MSNA then returned to resting levels within the first minute of recovery. Limb ischemia had no significant influence on the intensity-dependent rise in MSNA or its decline during recovery in the active leg. These findings reveal intensity-dependent increases in total MSNA and burst amplitude to contracting human skeletal muscle that do not appear to involve the muscle metaboreflex.
Keywords: contraction; ischemia; metaboreflex; muscle; sympathetic.
Figures
References
-
- Hansen J., Thomas G. D., Jacobsen T. N., Victor R. G. (1994). Muscle metaboreflex triggers parallel sympathetic activation in exercising and resting human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 266, H2508–H2514 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

