Biophysical analysis of the interaction of the serum protein human β2GPI with bacterial lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 24918058
- PMCID: PMC4050186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fob.2014.04.008
Biophysical analysis of the interaction of the serum protein human β2GPI with bacterial lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
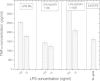
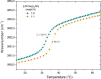
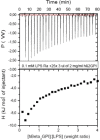
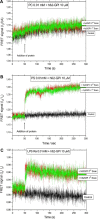
There are several human serum proteins for which no clear role is yet known. Among these is the abundant serum protein beta2-glycoprotein-I (β2GPI), which is known to bind to negatively charged phospholipids as well as to bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and was therefore proposed to play a role in the immune response. To understand the details of these interactions, a biophysical analysis of the binding of β2GPI to LPS and phosphatidylserine (PS) was performed. The data indicate only a moderate tendency of the protein (1) to influence the LPS-induced cytokine production in vitro, (2) to react exothermally with LPS in a non-saturable way, and (3) to change its local microenvironment upon LPS association. Additionally, we found that the protein binds more strongly to phosphatidylserine (PS) than to LPS. Furthermore, β2GPI converts the LPS bilayer aggregates into a stronger multilamellar form, and reduces the fluidity of the hydrocarbon moiety of LPS due to a rigidification of the acyl chains. From these data it can be concluded that β2GPI plays a role as an immune-modulating agent, but there is much less evidence for a role in immune defense against bacterial toxins such as LPS.
Keywords: Cytokine production; FRET, fluorescence resonance energy transfer spectroscopy; FTIR, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy; HDL, high-density lipoproteins; Human glycoprotein β2GPI; ITC, isothermal titration calorimetry; Immune modulation; LAL test; LAL, Limulus amebocyte lysate; LBP, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; LDL, low-density lipoproteins; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; Lipopolysaccharide; MNC, mononuclear cells; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PS, phosphatidylserine; SAXS, small-angle X-ray scattering; β2GPI, beta2-glycoprotein-I.
Figures


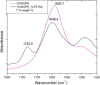
 O stretching vibration). The position of the peak maxima can be assigned to different secondary structures due to different water binding, i.e., α-helix between 1650 and 1655 cm−1, β-sheets between 1625 and 1640 cm−1, and a particular helical structure 310-helix between 1637 and 1643 cm−1.
O stretching vibration). The position of the peak maxima can be assigned to different secondary structures due to different water binding, i.e., α-helix between 1650 and 1655 cm−1, β-sheets between 1625 and 1640 cm−1, and a particular helical structure 310-helix between 1637 and 1643 cm−1.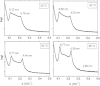
Similar articles
-
Biophysical characterization of the interaction of Limulus polyphemus endotoxin neutralizing protein with lipopolysaccharide.Eur J Biochem. 2004 May;271(10):2037-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04134.x. Eur J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15128313
-
Biophysical characterization of lipopolysaccharide and lipid A inactivation by lactoferrin.Biol Chem. 2001 Aug;382(8):1215-25. doi: 10.1515/BC.2001.152. Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11592403
-
Mechanism of interaction of optimized Limulus-derived cyclic peptides with endotoxins: thermodynamic, biophysical and microbiological analysis.Biochem J. 2007 Sep 1;406(2):297-307. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070279. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17501719 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of endotoxic activity in the Limulus test as compared to cytokine production in immune cells.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(21):2653-60. doi: 10.2174/092986709788682001. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19601802 Review.
-
β2-Glycoprotein I-Reactive T Cells in Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 10;9:2836. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02836. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The purification of reduced β2-glycoprotein I showed its native activity in vitro.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Sep 13;16(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0555-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28903783 Free PMC article.
-
The exopolysaccharide-eDNA interaction modulates 3D architecture of Bacillus subtilis biofilm.BMC Microbiol. 2020 May 14;20(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01789-5. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32410574 Free PMC article.
-
The exopolysaccharide Psl-eDNA interaction enables the formation of a biofilm skeleton in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015 Apr;7(2):330-40. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12252. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25472701 Free PMC article.
-
Gram Negative Bacterial Inflammation Ameliorated by the Plasma Protein Beta 2-Glycoprotein I.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 27;6:33656. doi: 10.1038/srep33656. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27670000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tapping R.I., Gegner J.A., Kravchenko V.V., Tobias P.S. Roles for LBP and soluble CD14 in cellular uptake of LPS. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1998;397:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Hammel M., Schwarzenbacher R., Gries A., Kostner G.M., Laggner P., Prassl R. Mechanism of the interaction of beta(2)-glycoprotein I with negatively charged phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 2001;40:14173–14181. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

