Myxozoa in high Arctic: Survey on the central part of Svalbard archipelago
- PMID: 24918076
- PMCID: PMC4047956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2014.02.001
Myxozoa in high Arctic: Survey on the central part of Svalbard archipelago
Abstract
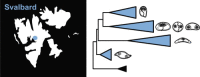
Myxosporeans (Myxozoa), microscopic metazoan parasitic organisms, are poorly studied in the Arctic region. Our survey of benthic and pelagic fish (n = 234) collected in Isfjorden (Svalbard, Norway) together with detailed morphological and molecular examination revealed the presence of nine myxosporean species. We compared observed myxosporean diversity with diversity documented in regions close to the Arctic and revealed that water depth rather than geographic distribution is an important factor influencing myxosporean fauna.
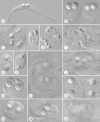
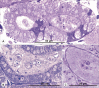
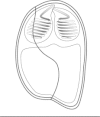
We describe three new myxosporean species: Zschokkella siegfriedi n. sp. from kidney of Boreogadus saida, Parvicapsula petuniae n. sp. from the urinary bladder of Gymnocanthus tricuspis, and Sinuolinea arctica n. sp. from the urinary bladder of Myoxocephalus scorpius. We characterise Latyspora-like organism from kidney of Clupea harengus. We provide new data for Ceratomyxa porrecta, Myxidium gadi, Myxidium finnmarchicum, Schulmania aenigmatosa, and Parvicapsula irregularis comb. nov. The phylogenetic analyses including the newly obtained SSU and LSU rDNA data revealed that most of the species studied cluster in the marine urinary clade within the marine myxosporean lineage. Newly obtained sequences including the first molecular data for the member of the genus Schulmania, substantially enriched the Zschokkella subclade. C. porrecta and the two Myxidium species cluster within the Ceratomyxa and marine Myxidium clade, respectively. Newly described species, Z. siegfriedi n. sp., was revealed to be morphologically indistinguishable but genetically diverse from Zschokkella hildae known from numerous gadid fish. Therefore, we consider Z. siegfriedi to be a cryptic myxosporean species that might be misidentified with Z. hildae. A Latyspora-like organism was found to be taxonomically problematic due to its suture line and its distant phylogenetic position from the type species Latyspora scomberomori did not allow us to assign it to the genus Latyspora. Based on an increased taxon sampling and SSU + LSU rDNA-based phylogeny, evolutionary trends within the marine urinary clade are investigated.
Keywords: Arctic; Marine urinary clade; Myxosporea; Phylogeny; Schulmania; Zschokkella.
Figures








References
-
- Arthur J.R., Lom J. Sphaerospora araii n. sp. (Myxosporea: Sphaerosporidae) from the kidney of a longnose skate (Raja rhina Jordan and Gilbert) from the Pacific Ocean off Canada. Can. J. Zool. 1985;63:2902–2906.
-
- Aseeva L.N. New species of myxosporeans (Myxozoa, Myxosporea) from sculpins of the northwestern Japan Sea. Acta Parasitol. 2002;47:179–189.
-
- Auerbach M. Biologische und morphologische Bemerkungen über Myxosporidien. Zool. Anzeiger. 1910;35:57–63.
-
- Avise J. second ed. Sinauer Associates; Sunderland (Massachusetts): 2004. Molecular markers, natural history, and evolution. p. 684.
-
- Barta J.R., Martin D.S., Liberator P.A., Dashkevicz M., Anderson J.W., Feighner S.D., Elbrecht A., Perkins-Barrow A., Jenkins M.C., Danforth H.D., Ruff M.D., Profous-Juchelka H. Phylogenetic relationships among eight Eimeria species infecting domestic fowl inferred using complete small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. J. Parasitol. 1997;83:262–271. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

