Albumin-induced podocyte injury and protection are associated with regulation of COX-2
- PMID: 24918154
- PMCID: PMC4245399
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2014.196
Albumin-induced podocyte injury and protection are associated with regulation of COX-2
Abstract
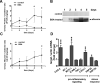
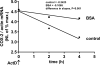
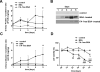
Albuminuria is both a hallmark and a risk factor for progressive glomerular disease, and results in increased exposure of podocytes to serum albumin with its associated factors. Here in vivo and in vitro models of serum albumin-overload were used to test the hypothesis that albumin-induced proteinuria and podocyte injury directly correlate with COX-2 induction. Albumin induced COX-2, MCP-1, CXCL1, and the stress protein HSP25 in both rat glomeruli and cultured podocytes, whereas B7-1 and HSP70i were also induced in podocytes. Podocyte exposure to albumin induced both mRNA and protein and enhanced the mRNA stability of COX-2, a key regulator of renal hemodynamics and inflammation, which renders podocytes susceptible to injury. Podocyte exposure to albumin also stimulated several kinases (p38 MAPK, MK2, JNK/SAPK, and ERK1/2), inhibitors of which (except JNK/SAPK) downregulated albumin-induced COX-2. Inhibition of AMPK, PKC, and NFκB also downregulated albumin-induced COX-2. Critically, albumin-induced COX-2 was also inhibited by glucocorticoids and thiazolidinediones, both of which directly protect podocytes against injury. Furthermore, specific albumin-associated fatty acids were identified as important contributors to COX-2 induction, podocyte injury, and proteinuria. Thus, COX-2 is associated with podocyte injury during albuminuria, as well as with the known podocyte protection imparted by glucocorticoids and thiazolidinediones. Moreover, COX-2 induction, podocyte damage, and albuminuria appear mediated largely by serum albumin-associated fatty acids.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Inhibition of the protein kinase MK-2 protects podocytes from nephrotic syndrome-related injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):F509-19. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00661.2010. Epub 2011 May 25. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21613416 Free PMC article.
-
Puromycin induces reversible proteinuric injury in transgenic mice expressing cyclooxygenase-2 in podocytes.Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2007;107(3):e87-94. doi: 10.1159/000108653. Epub 2007 Sep 21. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17890881
-
Fn14 in podocytes and proteinuric kidney disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2232-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.08.010. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23999007
-
Intracellular albumin overload elicits endoplasmic reticulum stress and PKC-delta/p38 MAPK pathway activation to induce podocyte apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 20;8(1):18012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36933-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30573754 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2, and prostanoid receptor EP2 in fluid flow shear stress-mediated injury in the solitary kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Dec 15;307(12):F1323-33. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00335.2014. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25234310
Cited by
-
Aspirin for the prevention and treatment of pre-eclampsia: A matter of COX-1 and/or COX-2 inhibition?Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020 Aug;127(2):132-141. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13308. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31420920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases.Oncotarget. 2018 May 29;9(41):26586-26602. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25005. eCollection 2018 May 29. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29899878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of downstream targets of p38 MAPK in experimental nephrotic syndrome.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;314(4):F602-F613. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00207.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29187369 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of myo-inositol oxygenase in AGE:RAGE-mediated renal tubulointerstitial injury in the context of diabetic nephropathy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):F107-F121. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00434.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28931523 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Glucocorticoid Receptors in Podocytes and Nephrotic Syndrome.Nucl Receptor Res. 2018;5:101323. doi: 10.11131/2018/101323. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Nucl Receptor Res. 2018. PMID: 30417008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iseki K, Ikemiya Y, Iseki C, et al. Proteinuria and the risk of developing end-stage renal disease. Kidney international. 2003;63:1468–1474. - PubMed
-
- Brunskill NJ. Albumin signals the coming of age of proteinuric nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:504–505. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence GM, Brewer DB. Effect of strain and sex on the induction of hyperalbuminaemic proteinuria in the rat. Clinical science. 1981;61:751–756. - PubMed
-
- Eddy AA, Kim H, Lopez-Guisa J, et al. Interstitial fibrosis in mice with overload proteinuria: deficiency of TIMP-1 is not protective. Kidney international. 2000;58:618–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

