No socioeconomic inequalities in ovarian cancer survival within two randomised clinical trials
- PMID: 24918817
- PMCID: PMC4119977
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.303
No socioeconomic inequalities in ovarian cancer survival within two randomised clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among cancers of the female genital tract, with poor outcomes despite chemotherapy. There was a persistent socioeconomic gradient in 1-year survival in England and Wales for more than 3 decades (1971-2001). Inequalities in 5-year survival persisted for more than 20 years but have been smaller for women diagnosed around 2000. We explored one possible explanation.
Methods: We analysed data on 1406 women diagnosed with ovarian cancer during 1991-1998 and recruited to one of two randomised clinical trials. In the second International Collaborative Ovarian Neoplasm (ICON2) trial, women diagnosed between 1991 and 1996 were randomised to receive either the three-drug combination cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and cisplatin (CAP) or single-agent carboplatin given at optimal dose. In the ICON3 trial, women diagnosed during 1995-1998 were randomised to receive either the same treatments as ICON2, or paclitaxel plus carboplatin.Relative survival at 1, 5 and 10 years was estimated for women in five categories of socioeconomic deprivation. The excess hazard of death over and above background mortality was estimated by fitting multivariable regression models with Poisson error structure and a dedicated link function in a generalised linear model framework, adjusting for the duration of follow-up and the confounding effects of age, Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage and calendar period.
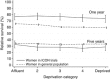
Results: Unlike women with ovarian cancer in the general population, no statistically significant socioeconomic gradient was seen for women with ovarian cancer treated in the two randomised controlled trials. The deprivation gap in 1-year relative survival in the general population was statistically significant at -6.7% (95% CI (-8.1, -5.3)), compared with -3.6% (95% CI (-10.4, +3.2)) in the trial population.
Conclusions: Although ovarian cancer survival is significantly lower among poor women than rich women in England and Wales, there was no evidence of an association between socioeconomic deprivation and survival among women with ovarian cancer who were treated and followed up consistently in two well-conducted randomised controlled trials. We conclude that the persistent socioeconomic gradient in survival among women with ovarian cancer, at least for 1-year survival, may be due to differences in access to treatment and standards of care.
Figures
References
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Tainsky MA, Abrams J, Severson RK, Qureshi F, Jacques SM, Levin N, Schwartz AG. Ethnic differences in survival among women with ovarian carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;94:1886–1893. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Research UK Cancer Survival Group 2004Life Tables for England and Wales by Sex, Calendar Period, Region and Deprivation London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine: London. http://www.lshtm.ac.uk/eph/ncde/cancersurvival/tools/index.html , accessed 16 Feburary 2009.
-
- Cancer Research UK Cancer Survival Group 2010strel Computer programme version 5.8 for Cancer Survival Analysis London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine: London. http://www.lshtm.ac.uk/eph/ncde/cancersurvival/tools/ , accessed 28 July 2011.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous