Individual differences in ethanol locomotor sensitization are associated with dopamine D1 receptor intra-cellular signaling of DARPP-32 in the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 24919054
- PMCID: PMC4053371
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098296
Individual differences in ethanol locomotor sensitization are associated with dopamine D1 receptor intra-cellular signaling of DARPP-32 in the nucleus accumbens
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e103667
- PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e104151
Abstract
In mice there are clear individual differences in the development of behavioral sensitization to ethanol, a progressive potentiation of its psychomotor stimulant effect. Variability in the behavioral responses to ethanol has been associated with alcohol preference. Here we investigated if the functional hyperresponsiveness of D1 receptors observed in ethanol sensitized mice leads to an increased activation of DARPP-32, a central regulatory protein in medium spiny neurons, in the nucleus accumbens - a brain region known to play a role in drug reinforcement. Swiss Webster mice received ethanol (2.2 g/kg/day) or saline i.p. administrations for 21 days and were weekly evaluated regarding their locomotor activity. From those treated with ethanol, the 33% with the highest levels of locomotor activity were classified as "sensitized" and the 33% with the lowest levels as "non-sensitized". The latter presented similar locomotor levels to those of saline-treated mice. Different subgroups of mice received intra-accumbens administrations of saline and, 48 h later, SKF-38393, D1 receptor agonist 0.1 or 1 µg/side. Indeed, sensitized mice presented functional hyperresponsiveness of D1 receptors in the accumbens. Two weeks following the ethanol treatment, other subgroups received systemic saline or SKF 10 mg/kg, 20 min before the euthanasia. The nucleus accumbens were dissected for the Western Blot analyses of total DARPP-32 and phospho-Thr34-DARPP-32 expression. D1 receptor activation induced higher phospho-Thr34-DARPP-32 expression in sensitized mice than in non-sensitized or saline. The functionally hyperresponsiveness of D1 receptors in the nucleus accumbens is associated with an increased phospho-Thr34-DARPP-32 expression after D1 receptor activation. These data suggest that an enduring increase in the sensitivity of the dopamine D1 receptor intracellular pathway sensitivity represents a neurobiological correlate associated with the development of locomotor sensitization to ethanol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


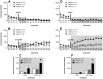
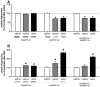
References
-
- Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, et al. (2009) Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 373: 2223–2233. - PubMed
-
- Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Lumeng L, Murphy JM, McBride WJ (2006) The alcohol-preferring P rat and animal models of excessive alcohol drinking. Addict Biol 11: 270–288. - PubMed
-
- Lessov CN, Palmer AA, Quick EA, Phillips TJ (2001) Voluntary ethanol drinking in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice before and after sensitization to the locomotor stimulant effects of ethanol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 155: 91–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

