External validation of a prognostic model for seizure recurrence following a first unprovoked seizure and implications for driving
- PMID: 24919184
- PMCID: PMC4053525
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099063
External validation of a prognostic model for seizure recurrence following a first unprovoked seizure and implications for driving
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e113327
Abstract
Objective: In the United Kingdom and other European Union countries guidelines for driving following a first unprovoked seizure require the risk of another seizure in the next year to be less than 20%. Using data from one clinical trial, we previously developed a prognostic model to inform driving guidelines. The objective of this work is to externally validate our published model and demonstrate its generalisability.
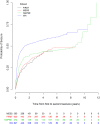
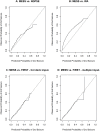
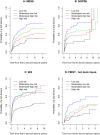
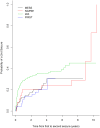
Methods: A cohort of 620 people with a first unprovoked seizure was used to develop the original model which included variables for aetiology, first degree relative with epilepsy, seizures only while asleep, electroencephalogram, computed tomography or magnetic resonance scan result, and treatment policy. The validation cohorts consisted of 274 (United Kingdom), 305 (Italy), and 847 (Australia) people. The model was evaluated using discrimination and calibration methods. A covariate, missing from the Italian dataset, was handled via five imputation methods. Following external validation, the model was fitted to a pooled population comprising all validation datasets and the development dataset. The model was stratified by dataset.
Results: The model generalised relatively well. All methods of imputation performed fairly similarly. At six months, the risk of a seizure recurrence following a first ever seizure, based on the pooled datasets, is 15% (95% CI: (12% to 18%)) for patients who are treated immediately and 18% (95% CI: (15 to 21%)) otherwise. Individuals can be reliably stratified into risk groups according to the clinical factors included in the model.
Significance: Our prognostic model, used to inform driving regulations, has been validated and consequently has been proven as a valuable tool for predicting risk of seizure recurrence following a first seizure in people with various combinations of risk factors. Additionally, there is evidence to support one worldwide overall prognostic model for risk of second seizure following a first.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Marson A, Jacoby A, Johnson A, Kim L, Gamble C, et al. (2005) Immediate versus deferred antiepileptic drug treatment for early epilepsy and single seizures: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 365: 2007–2013. - PubMed
-
- Kim LG, Johnson TL, Marson AG, Chadwick DW (2006) Prediction of Risk of Seizure Recurrence after a Single Seizure and Early Epilepsy: Further Results from the MESS Trial. The Lancet Neurology 5: 317–322. - PubMed
-
- Steyerberg EW (2009) Clinical Prediction Models. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, LLC.
-
- Hart YM, Sander JWAS, Shorvon SD (1989) National General-Practice Study of Epilepsy and Epileptic Seizures - Objectives and Study Methodology of the Largest Reported Prospective Cohort Study of Epilepsy. Neuroepidemiology 8: 221–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

