Ron receptor-dependent gene regulation of Kupffer cells during endotoxemia
- PMID: 24919612
- PMCID: PMC4108450
- DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(14)60254-x
Ron receptor-dependent gene regulation of Kupffer cells during endotoxemia
Abstract
Background: Ron receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in macrophages, including Kupffer cells and alveolar macrophages, suppresses endotoxin-induced proinflammatory cytokine/chemokine production. Further, we have also identified genes from Ron replete and Ron deplete livers that were differentially expressed during the progression of liver inflammation associated with acute liver failure in mice by microarray analyses. While important genes and signaling pathways have been identified downstream of Ron signaling during progression of inflammation by this approach, the precise role that Ron receptor plays in regulating the transcriptional landscape in macrophages, and particular in isolated Kupffer cells, has still not been investigated.
Methods: Kupffer cells were isolated from wild-type (TK+/+) and Ron tyrosine kinase deficient (TK-/-) mice. Ex vivo, the cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the presence or absence of the Ron ligand, hepatocyte growth factor-like protein (HGFL). Microarray and qRT-PCR analyses were utilized to identify alterations in gene expression between genotypes.
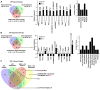
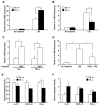
Results: Microarray analyses identified genes expressed differentially in TK+/+ and TK-/- Kupffer cells basally as well as after HGFL and LPS treatment. Interestingly, our studies identified Mefv, a gene that codes for the anti-inflammatory protein pyrin, as an HGFL-stimulated Ron-dependent gene. Moreover, lipocalin 2, a proinflammatory gene, which is induced by LPS, was significantly suppressed by HGFL treatment. Microarray results were validated by qRT-PCR studies on Kupffer cells treated with LPS and HGFL.
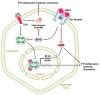
Conclusion: The studies herein suggest a novel mechanism whereby HGFL-induced Ron receptor activation promotes the expression of anti-inflammatory genes while inhibiting genes involved in inflammation with a net effect of diminished inflammation in macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Hansson GK, Hermansson A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:204–212. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkbacka H, Fitzgerald KA, Huet F, Li X, Gregory JA, Lee MA, et al. The induction of macrophage gene expression by LPS predominantly utilizes Myd88-independent signaling cascades. Physiol Genomics. 2004;19:319–330. - PubMed
-
- Okino T, Egami H, Ohmachi H, Takai E, Tamori Y, Nakagawa A, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of distribution of RON receptor tyrosine kinase in human digestive organs. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46:424–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

