Hydroxyl fasudil, an inhibitor of Rho signaling, improves erectile function in diabetic rats: a role for neuronal ROCK
- PMID: 24919622
- PMCID: PMC4230280
- DOI: 10.1111/jsm.12613
Hydroxyl fasudil, an inhibitor of Rho signaling, improves erectile function in diabetic rats: a role for neuronal ROCK
Abstract
Introduction: The pathogenesis of diabetic erectile dysfunction (ED) includes neuropathy, but the molecular basis for neurogenic ED is incompletely understood. The RhoA/ROCK pathway has been implicated in diabetic neuropathy and in ED, but its role in diabetic neurogenic ED is not known.
Aims: The aim of this study was to determine whether hydroxyl fasudil, a ROCK inhibitor, affects diabetic neuropathy-related ED.
Methods: Type 1 diabetes mellitus was induced in male rats by streptozotocin (75 mg/kg, intraperitoneally). After 8 weeks, diabetic rats were administered hydroxyl fasudil, a selective ROCK inhibitor (10 mg/kg/day, intraperitoneally) or vehicle, for 4 weeks. Age-matched control, nondiabetic, rats were treated intraperitoneally for 4 weeks with saline. At week 12, after a 2 day washout, neuro-stimulated erectile function was evaluated. Major pelvic ganglia (MPG) were collected for Western blot analysis of RhoA, ROCK-1, ROCK-2, phospho (P)-AKT (Ser(473) ), and P-phosphatase and tensin homolog (P-PTEN) (Ser(380) /Thr(382/383) ).
Main outcome measures: Effect of ROCK inhibitor hydroxyl fasudil on erectile function and ROCK/P-AKT/P-PTEN pathway in the MPG of diabetic rats.
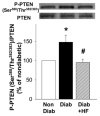
Results: Erectile response was significantly (P < 0.05) reduced in diabetic rats compared with nondiabetic rats and was preserved (P < 0.05) in diabetic rats treated with hydroxyl fasudil. In diabetic rats, RhoA and ROCK-2 protein expressions in MPG were increased (P < 0.05) and remained increased in hydroxyl fasudil-treated rats. P-AKT (Ser(473) ) expression was decreased (P < 0.05), whereas P-PTEN (Ser(380) /Thr(382/383) ) expression was increased (P < 0.05) in MPG of diabetic rats compared with nondiabetic rats, and both were reversed (P < 0.05) in diabetic rats treated with hydroxyl fasudil.
Conclusion: Improved erectile function and restored P-AKT and P-PTEN in the MPG with hydroxyl fasudil treatment suggest the role of Rho signaling via PTEN/AKT pathway in neurogenic diabetic ED.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Diabetic Neuropathy; Major Pelvic Ganglia; P-AKT; P-PTEN.
© 2014 International Society for Sexual Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures



References
-
- Bacon CG, Hu FB, Giovannucci E, Glasser DB, Mittleman MA, Rimm EB. Association of type and duration of diabetes with erectile dysfunction in a large cohort of men. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1458–1463. - PubMed
-
- Cellek S. Point of NO return for nitrergic nerves in diabetes: a new insight into diabetic complications. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:3683–3695. - PubMed
-
- El-Sakka AI, Lin CS, Chui RM, Dahiya R, Lue TF. Effects of diabetes on nitric oxide synthase and growth factor genes and protein expression in an animal model. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Podlasek CA, Zelner DJ, Bervig TR, Gonzalez CM, McKenna KE, McVary KT. Characterization and localization of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in the BB/WOR diabetic rat. J Urol. 2001;166:746–755. - PubMed
-
- Vernet D, Cai L, Garban H, Babbitt ML, Murray FT, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF. Reduction of penile nitric oxide synthase in diabetic BB/WORdp (type I) and BBZ/WORdp (type II) rats with erectile dysfunction. Endocrinology. 1995;136:5709–5717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

