CNS amyloid-β, soluble APP-α and -β kinetics during BACE inhibition
- PMID: 24920637
- PMCID: PMC4051982
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0540-14.2014
CNS amyloid-β, soluble APP-α and -β kinetics during BACE inhibition
Abstract
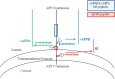
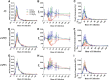
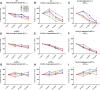
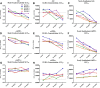
BACE, a β-secretase, is an attractive potential disease-modifying therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease (AD) as it results directly in the decrease of amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing through the β-secretase pathway and a lowering of CNS amyloid-β (Aβ) levels. The interaction of the β-secretase and α-secretase pathway-mediated processing of APP in the rhesus monkey (nonhuman primate; NHP) CNS is not understood. We hypothesized that CNS inhibition of BACE would result in decreased newly generated Aβ and soluble APPβ (sAPPβ), with increased newly generated sAPPα. A stable isotope labeling kinetics experiment in NHPs was performed with a (13)C6-leucine infusion protocol to evaluate effects of BACE inhibition on CNS APP processing by measuring the kinetics of sAPPα, sAPPβ, and Aβ in CSF. Each NHP received a low, medium, or high dose of MBI-5 (BACE inhibitor) or vehicle in a four-way crossover design. CSF sAPPα, sAPPβ, and Aβ were measured by ELISA and newly incorporated label following immunoprecipitation and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Concentrations, kinetics, and amount of newly generated APP fragments were calculated. sAPPβ and sAPPα kinetics were similar, but both significantly slower than Aβ. BACE inhibition resulted in decreased labeled sAPPβ and Aβ in CSF, without observable changes in labeled CSF sAPPα. ELISA concentrations of sAPPβ and Aβ both decreased and sAPPα increased. sAPPα increased by ELISA, with no difference by labeled sAPPα kinetics indicating increases in product may be due to APP shunting from the β-secretase to the α-secretase pathway. These results provide a quantitative understanding of pharmacodynamic effects of BACE inhibition on NHP CNS, which can inform about target development.
Keywords: BACE inhibitor; SILK; amyloid beta; amyloid precursor protein; sAPPα; sAPPβ.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/348336-11$15.00/0.
Figures


References
-
- Alexopoulos P, Tsolakidou A, Roselli F, Arnold A, Grimmer T, Westerteicher C, Leante MR, Förstl H, Livrea P, Kurz A, Perneczky R. Clinical and neurobiological correlates of soluble amyloid precursor proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;8:304–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.04.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bateman RJ, Siemers ER, Mawuenyega KG, Wen G, Browning KR, Sigurdson WC, Yarasheski KE, Friedrich SW, Demattos RB, May PC, Paul SM, Holtzman DM. A gamma-secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-β production in the central nervous system. Ann Neurol. 2009;66:48–54. doi: 10.1002/ana.21623. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernier F, Sato Y, Matijevic M, Desmond H, McGrath S, Burns L, Kaplow JM, Albala B. Clinical study of E2609, a novel BACE1 inhibitor, demonstrates target engagement and inhibition of BACE1 activity in CSF. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:P886. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.08.244. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
