Macrophage models of Gaucher disease for evaluating disease pathogenesis and candidate drugs
- PMID: 24920659
- PMCID: PMC4161206
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008659
Macrophage models of Gaucher disease for evaluating disease pathogenesis and candidate drugs
Abstract
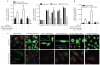
Gaucher disease is caused by an inherited deficiency of glucocerebrosidase that manifests with storage of glycolipids in lysosomes, particularly in macrophages. Available cell lines modeling Gaucher disease do not demonstrate lysosomal storage of glycolipids; therefore, we set out to develop two macrophage models of Gaucher disease that exhibit appropriate substrate accumulation. We used these cellular models both to investigate altered macrophage biology in Gaucher disease and to evaluate candidate drugs for its treatment. We generated and characterized monocyte-derived macrophages from 20 patients carrying different Gaucher disease mutations. In addition, we created induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived macrophages from five fibroblast lines taken from patients with type 1 or type 2 Gaucher disease. Macrophages derived from patient monocytes or iPSCs showed reduced glucocerebrosidase activity and increased storage of glucocerebroside and glucosylsphingosine in lysosomes. These macrophages showed efficient phagocytosis of bacteria but reduced production of intracellular reactive oxygen species and impaired chemotaxis. The disease phenotype was reversed with a noninhibitory small-molecule chaperone drug that enhanced glucocerebrosidase activity in the macrophages, reduced glycolipid storage, and normalized chemotaxis and production of reactive oxygen species. Macrophages differentiated from patient monocytes or patient-derived iPSCs provide cellular models that can be used to investigate disease pathogenesis and facilitate drug development.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Grabowski GA, Beutler E. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2001. pp. 3635–3668.
-
- Orvisky E, Park JK, LaMarca ME, Ginns EI, Martin BM, Tayebi N, Sidransky E. Glucosylsphingosine accumulation in tissues from patients with Gaucher disease: Correlation with phenotype and genotype. Mol Genet Metab. 2002;76:262–270. - PubMed
-
- Sidransky E, Nalls MA, Aasly JO, Aharon-Peretz J, Annesi G, Barbosa ER, Bar-Shira A, Berg D, Bras J, Brice A, Chen CM, Clark LN, Condroyer C, De Marco EV, Dürr A, Eblan MJ, Fahn S, Farrer MJ, Fung HC, Gan-Or Z, Gasser T, Gershoni-Baruch R, Giladi N, Griffith A, Gurevich T, Januario C, Kropp P, Lang AE, Lee-Chen GJ, Lesage S, Marder K, Mata IF, Mirelman A, Mitsui J, Mizuta I, Nicoletti G, Oliveira C, Ottman R, Orr-Urtreger A, Pereira LV, Quattrone A, Rogaeva E, Rolfs A, Rosenbaum H, Rozenberg R, Samii A, Samaddar T, Schulte C, Sharma M, Singleton A, Spitz M, Tan EK, Tayebi N, Toda T, Troiano AR, Tsuji S, Wittstock M, Wolfsberg TG, Wu YR, Zabetian CP, Zhao Y, Ziegler SG. Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1651–1661. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gardai SJ, McPhillips KA, Frasch SC, Janssen WJ, Starefeldt A, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Bratton DL, Oldenborg PA, Michalak M, Henson PM. Cell-surface calreticulin initiates clearance of viable or apoptotic cells through trans-activation of LRP on the phagocyte. Cell. 2005;123:321–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

