Malignant pleural effusion: medical approaches for diagnosis and management
- PMID: 24920947
- PMCID: PMC4050068
- DOI: 10.4046/trd.2014.76.5.211
Malignant pleural effusion: medical approaches for diagnosis and management
Abstract
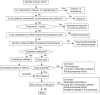
Malignant pleural effusions (MPEs) are the second leading cause of exudative pleural effusions after parapneumonic effusions. In the vast majority of cases, a MPE signifies incurable disease associated with high morbidity and mortality. Considerable advances have been made for the diagnosis of MPEs, through the development of improved methods in the specialized cytological and imaging studies. The cytological or histological confirmation of malignant cells is currently important in establishing a diagnosis. Furthermore, despite major advancements in cancer treatment for the past two decades, management of MPE remains palliative. This article presents a comprehensive review of the medical approaches for diagnosis and management of MPE.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Disease Management; Pleural Effusion, Malignant.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Thomas JM, Musani AI. Malignant pleural effusions: a review. Clin Chest Med. 2013;34:459–471. - PubMed
-
- Light RW. Pleural diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
-
- Heffner JE, Klein JS. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:235–250. - PubMed
-
- Heffner JE, Nietert PJ, Barbieri C. Pleural fluid pH as a predictor of survival for patients with malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 2000;117:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Bielsa S, Salud A, Martinez M, Esquerda A, Martin A, Rodriguez-Panadero F, et al. Prognostic significance of pleural fluid data in patients with malignant effusion. Eur J Intern Med. 2008;19:334–339. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous