Unique Responses are Observed in Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 and Vanilloid 1 (TRPA1 and TRPV1) Co-Expressing Cells
- PMID: 24921186
- PMCID: PMC4092848
- DOI: 10.3390/cells3020616
Unique Responses are Observed in Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 and Vanilloid 1 (TRPA1 and TRPV1) Co-Expressing Cells
Abstract
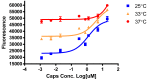
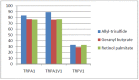
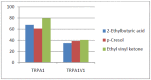
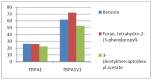
Transient receptor potential (TRP) ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) and vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptors are implicated in modulation of cough and nociception. In vivo, TRPA1 and TRPV1 are often co-expressed in neurons and TRPA1V1 hetero-tetramer formation is noted in cells co-transfected with the respective expression plasmids. In order to understand the impact of TRP receptor interaction on activity, we created stable cell lines expressing the TRPA1, TRPV1 and co-expressing the TRPA1 and TRPV1 (TRPA1V1) receptors. Among the 600 compounds screened against these receptors, we observed a number of compounds that activated the TRPA1, TRPV1 and TRPA1V1 receptors; compounds that activated TRPA1 and TRPA1V1; compounds that activated TRPV1 and TRPA1V1; compounds in which TRPA1V1 response was modulated by either TRPA1 or TRPV1; and compounds that activated only TRPV1 or TRPA1 or TRPA1V1; and one compound that activated TRPA1 and TRPV1, but not TRPA1V1. These results suggest that co-expression of TRPA1 and TRPV1 receptors imparts unique activation profiles different from that of cells expressing only TRPA1 or TRPV1.
Figures





References
-
- Story G.M., Peier A.M., Reeve A.J., Eid S.R., Mosbacher J., Hricik T.R., Earley T.J., Hergarden A.C., Andersson D.A., Hwang S.W., et al. ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell. 2003;112:819–829. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00158-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

