The ufm1 cascade
- PMID: 24921187
- PMCID: PMC4092871
- DOI: 10.3390/cells3020627
The ufm1 cascade
Abstract
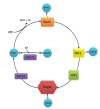
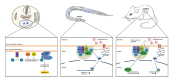
The ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (Ufm1) is a posttranslational modifier that belongs to the ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) family. Ufm1 is present in nearly all eukaryotic organisms, with the exception of fungi. It resembles ubiquitin in its ability to be ligated to other proteins, as well as in the mechanism of ligation. While the Ufm1 cascade has been implicated in endoplasmic reticulum functions and cell cycle control, its biological role still remains poorly understood. In this short review, we summarize the current state of Ufm1 research and its potential role in human diseases, like diabetes, ischemic heart disease and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Cort J.R., Chiang Y., Zheng D., Montelione G.T., Kennedy M.A. Nmr structure of conserved eukaryotic protein zk652.3 from c. Elegans: A ubiquitin-like fold. Proteins. 2002;48:733–736. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

