Abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life questionnaire (WHOQOL-Bref) in north Indian patients with bronchial asthma: an evaluation using Rasch analysis
- PMID: 24921608
- PMCID: PMC4373256
- DOI: 10.1038/npjpcrm.2014.1
Abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life questionnaire (WHOQOL-Bref) in north Indian patients with bronchial asthma: an evaluation using Rasch analysis
Abstract
Background: There is no disease-specific instrument to describe health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in Indian patients with asthma. However, an abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life questionnaire (WHOQOL-Bref), a generic Hindi HRQoL measure, has been developed and validated in India.
Aims: To evaluate the WHOQOL-Bref in adult patients with asthma and to test possible modifications to the instrument to improve its psychometric adequacy.
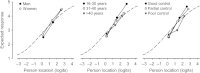
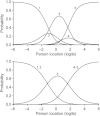
Methods: Sixty-seven patients with asthma completed the WHOQOL-Bref. Rasch analysis was used to explore the psychometric performance of the four domains (physical, psychological, social relationships and environment) of the scale. Overall fit of data to model expectations, appropriate category ordering, presence of differential item functioning, individual item fit and targeting of item difficulty to patient ability were explored for each domain. Item deletion and rescoring were applied to misfitting items to improve overall performance.
Results: The overall fit of the WHOQOL-Bref data was adequate. Item 3 (pain prevents doing work) displayed a large positive fit residual value (indicating violation of unidimensionality), resulting in poor construct validity for the physical domain. No item exhibited differential item functioning. Ten items had disordered thresholds. The WHOQOL-Bref was modified by dropping item 3 and rescoring category structures of 16 items. The modified scale had good construct validity for all domains, ordered thresholds for all items and good targeting of items to persons.
Conclusions: The WHOQOL-Bref performed inadequately in describing HRQoL in the asthma patients studied. However, when modified by Rasch analysis, the scale proved better than the original scale.
Figures

References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma Global strategy for asthma management and prevention . http://www.ginasthma.org , 2012
-
- Aggarwal AN, Agarwal R, Gupta D, Jindal SK. Validation of a Hindi translation of Mini Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire in north Indian patients with bronchial asthma. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2010;52:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Saxena S, Chandiramani K, Bhargava R. WHOQOL-Hindi: a questionnaire for assessing quality of life in health care settings in India. World Health Organization Quality of Life. Natl Med J India. 1998;11:160–165. - PubMed
-
- Saxena S, Quinn K, Sharan P, Naresh B, Yuantao H, Power M. Cross-linguistic equivalence of WHOQOL-100: a study from North India. Qual Life Res. 2005;14:891–897. - PubMed
-
- Tennant A, McKenna SP, Hagell P. Application of Rasch analysis in the development and application of quality of life instruments. Value Health. 2004;7 (Suppl 1):S22–S26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

