Upregulation of BDNF and NGF in cervical intervertebral discs exposed to painful whole-body vibration
- PMID: 24921856
- PMCID: PMC4149599
- DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000457
Upregulation of BDNF and NGF in cervical intervertebral discs exposed to painful whole-body vibration
Abstract
Study design: In vivo study defining expression of the neurotrophins, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF), in cervical intervertebral discs after painful whole-body vibration (WBV).
Objective: The goal of this study is to determine if BDNF and NGF are expressed in cervical discs after painful WBV in a rat model.
Summary of background data: WBV is a possible source of neck pain and has been implicated as increasing the risk for disc disorders. Typically, aneural regions of painful human lumbar discs exhibit hyperinnervation, suggesting nerve ingrowth as potentially contributing to disc degeneration and pain. BDNF and NGF are upregulated in painfully degenerate lumbar discs and hypothesized to contribute to this pathology.
Methods: Male Holtzman rats underwent 7 days of repeated WBV (15 Hz, 30 min/d) or sham exposures, followed by 7 days of rest. Cervical discs were collected for analysis of BDNF and NGF expression through RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis. Immunohistochemistry also evaluated their regional expression in the disc.
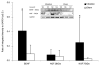
Results: Vibration significantly increases BDNF messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) levels (P=0.036), as well as total-NGF mRNA (P=0.035). Protein expression of both BDNF (P=0.006) and the 75-kDa NGF (P=0.045) increase by nearly 4- and 10-fold, respectively. Both BDNF mRNA (R=0.396; P=0.012) and protein (R=0.280; P=0.035) levels are significantly correlated with the degree of behavioral sensitivity (i.e., pain) at day 14. Total-NGF mRNA is also significantly correlated with the extent of behavioral sensitivity (R=0.276; P=0.044). Both neurotrophins are most increased in the inner annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus.
Conclusion: The increases in BDNF and NGF in the cervical discs after painful vibration are observed in typically aneural regions of the disc, consistent with reports of its hyperinnervation. Yet, the induction of nerve ingrowth into the disc was not explicitly investigated. Neurotrophin expression also correlates with behavioral sensitivity, suggesting a role for both neurotrophins in the development of disc pain.
Level of evidence: N/A.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression and regulation of neurotrophins in the nondegenerate and degenerate human intervertebral disc.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R99. doi: 10.1186/ar2487. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18727839 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of neurotrophic factors in the dorsal root ganglion in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation.Pain. 2002 Sep;99(1-2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(02)00068-4. Pain. 2002. PMID: 12237190
-
Expression and regulation of neurotrophic and angiogenic factors during human intervertebral disc degeneration.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Aug 20;16(5):416. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0416-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25209447 Free PMC article.
-
Partners in Crime: NGF and BDNF in Visceral Dysfunction.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(11):1021-1038. doi: 10.2174/1570159X17666190617095844. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31204623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NGF and BDNF in pediatrics syndromes.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 Feb;145:105015. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.105015. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 36563920 Review.
Cited by
-
Looking beyond the intervertebral disc: the need for behavioral assays in models of discogenic pain.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Dec;1409(1):51-66. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13429. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28797134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Regeneration: New Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutics: Obstacles and Potential Breakthrough Technologies.Cells. 2024 Dec 19;13(24):2103. doi: 10.3390/cells13242103. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39768194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Should you adjust that herniated disc? Thoughts from a chiropractor/molecular scientist.J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2023 Apr;67(1):7-18. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37250457 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular nerve growth factor regulates development, but not maintenance, of injury-induced facet joint pain & spinal neuronal hypersensitivity.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015 Nov;23(11):1999-2008. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.06.012. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015. PMID: 26521746 Free PMC article.
-
A Single Injection of NTG-101 Reduces the Expression of Pain-Related Neurotrophins in a Canine Model of Degenerative Disc Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 20;23(10):5717. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105717. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bovenzi M, Hulshof C. An updated review of epidemiological studies on the relationship between exposure to whole-body vibration and low back pain. J Sound Vib. 1998;215:595–613.
-
- Pope M, Magnusson M, Lundstrom R, et al. Guidelines for whole body vibration health surveillance. J Sound Vib. 2002;253:131–67.
-
- Gregory DE, Callaghan JP. Does vibration influence the initiation of intervertebral disc herniation? Spine. 36:E225–31. - PubMed
-
- Milosavljevic S, Bagheri N, Vasiljev RM, et al. Does daily exposure to whole-body vibration and mechanical shock relate to the prevalence of low back and neck pain in a rural workforce? Ann Occup Hyg. 2012;56:10–7. - PubMed
-
- Rehn B, Nilsson T, Lundström R, et al. Neck pain combined with arm pain among professional drivers of forest machines and the association with whole-body vibration exposure. Ergonomics. 2009;52:1240–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

