BioAssemblyModeler (BAM): user-friendly homology modeling of protein homo- and heterooligomers
- PMID: 24922057
- PMCID: PMC4055448
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098309
BioAssemblyModeler (BAM): user-friendly homology modeling of protein homo- and heterooligomers
Abstract
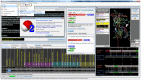
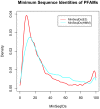
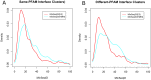
Many if not most proteins function in oligomeric assemblies of one or more protein sequences. The Protein Data Bank provides coordinates for biological assemblies for each entry, at least 60% of which are dimers or larger assemblies. BioAssemblyModeler (BAM) is a graphical user interface to the basic steps in homology modeling of protein homooligomers and heterooligomers from the biological assemblies provided in the PDB. BAM takes as input up to six different protein sequences and begins by assigning Pfam domains to the target sequences. The program utilizes a complete assignment of Pfam domains to sequences in the PDB, PDBfam (http://dunbrack2.fccc.edu/protcid/pdbfam), to obtain templates that contain any or all of the domains assigned to the target sequence(s). The contents of the biological assemblies of potential templates are provided, and alignments of the target sequences to the templates are produced with a profile-profile alignment algorithm. BAM provides for visual examination and mouse-editing of the alignments supported by target and template secondary structure information and a 3D viewer of the template biological assembly. Side-chain coordinates for a model of the biological assembly are built with the program SCWRL4. A built-in protocol navigation system guides the user through all stages of homology modeling from input sequences to a three-dimensional model of the target complex.
Availability: http://dunbrack.fccc.edu/BAM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Koh GC, Porras P, Aranda B, Hermjakob H, Orchard SE (2012) Analyzing protein-protein interaction networks. J Proteome Res 11: 2014–2031. - PubMed
-
- Traut TW (1994) Dissociation of enzyme oligomers: a mechanism for allosteric regulation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 29: 125–163. - PubMed
-
- Gray JJ, Moughon S, Wang C, Schueler-Furman O, Kuhlman B, et al. (2003) Protein-protein docking with simultaneous optimization of rigid-body displacement and side-chain conformations. J Mol Biol 331: 281–299. - PubMed
-
- Mosca R, Ceol A, Aloy P (2013) Interactome3D: adding structural details to protein networks. Nat Methods 10: 47–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

