Identification of a natural product-like STAT3 dimerization inhibitor by structure-based virtual screening
- PMID: 24922077
- PMCID: PMC4611723
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.250
Identification of a natural product-like STAT3 dimerization inhibitor by structure-based virtual screening
Abstract
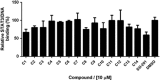
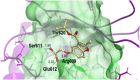
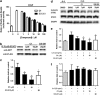
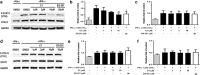
STAT3 regulates a variety of genes involved with cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, metastasis, inflammation, and immunity. The purpose of this study was to apply molecular docking techniques to identify STAT3 inhibitors from a database of over 90000 natural product and natural product-like compounds. The virtual screening campaign furnished 14 hit compounds, from which compound 1 emerged as a top candidate. Compound 1 inhibited STAT3 DNA-binding activity in vitro and attenuated STAT3-directed transcription in cellulo with selectivity over STAT1 and with comparable potency to the well-known STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201. Furthermore, compound 1 inhibited STAT3 dimerization and decreased STAT3 phosphorylation in cells without affecting STAT1 dimerization and phosphorylation. Compound 1 also exhibited selective anti-proliferative activity against cancer cells over normal cells in vitro. Molecular docking analysis suggested that compound 1 might putatively function as an inhibitor of STAT3 dimerization by binding to the SH2 domain. This study also validates the use of in silico techniques to identify inhibitors of protein-protein interactions, which are typically considered difficult to target with small molecules.
Figures

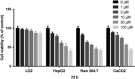
References
-
- 3Frank DA. STAT3 as a central mediator of neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett 2007; 251: 199–210. - PubMed
-
- 5Lai R, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ, Leventaki V, Keating M, McDonnell TJ. Expression of STAT3 and its phosphorylated forms in mantle cell lymphoma cell lines and tumours. J Pathol 2003; 199: 84–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

