Hypoxia-induced changes in protein s-nitrosylation in female mouse brainstem
- PMID: 24922346
- PMCID: PMC4370248
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0359OC
Hypoxia-induced changes in protein s-nitrosylation in female mouse brainstem
Abstract
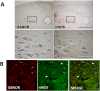
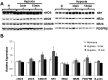
Exposure to hypoxia elicits an increase in minute ventilation that diminishes during continued exposure (roll-off). Brainstem N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) contribute to the initial hypoxia-induced increases in minute ventilation. Roll-off is regulated by platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β (PDGFR-β) and S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) reductase (GSNOR). S-nitrosylation inhibits activities of NMDAR and nNOS, but enhances GSNOR activity. The importance of S-nitrosylation in the hypoxic ventilatory response is unknown. This study confirms that ventilatory roll-off is virtually absent in female GSNOR(+/-) and GSNO(-/-) mice, and evaluated the location of GSNOR in female mouse brainstem, and temporal changes in GSNOR activity, protein expression, and S-nitrosylation status of GSNOR, NMDAR (1, 2A, 2B), nNOS, and PDGFR-β during hypoxic challenge. GSNOR-positive neurons were present throughout the brainstem, including the nucleus tractus solitarius. Protein abundances for GSNOR, nNOS, all NMDAR subunits and PDGFR-β were not altered by hypoxia. GSNOR activity and S-nitrosylation status temporally increased with hypoxia. In addition, nNOS S-nitrosylation increased with 3 and 15 minutes of hypoxia. Changes in NMDAR S-nitrosylation were detected in NMDAR 2B at 15 minutes of hypoxia. No hypoxia-induced changes in PDGFR-β S-nitrosylation were detected. However, PDGFR-β phosphorylation increased in the brainstems of wild-type mice during hypoxic exposure (consistent with roll-off), whereas it did not rise in GSNOR(+/-) mice (consistent with lack of roll-off). These data suggest that: (1) S-nitrosylation events regulate hypoxic ventilatory response; (2) increases in S-nitrosylation of NMDAR 2B, nNOS, and GSNOR may contribute to ventilatory roll-off; and (3) GSNOR regulates PDGFR-β phosphorylation.
Keywords: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; S-nitrosoglutathione reductase; hypoxic ventilatory response; neuronal nitric oxide synthase; platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β.
Figures



References
-
- Lahiri S, Roy A, Baby SM, Hoshi T, Semenza GL, Prabhakar NR. Oxygen sensing in the body. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006;91:249–286. - PubMed
-
- Teppema LJ, Dahan A. The ventilatory response to hypoxia in mammals: mechanisms, measurement, and analysis. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:675–754. - PubMed
-
- Gozal D, Torres JE, Gozal YM, Littwin SM. Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on cardiorespiratory responses in the conscious rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1996;81:2068–2077. - PubMed
-
- Gozal D, Gozal E, Simakajornboon N. Signaling pathways of the acute hypoxic ventilatory response in the nucleus tractus solitarius. Respir Physiol. 2000;121:209–221. - PubMed
-
- Gozal D, Simakajornboon N, Czapla MA, Xue YD, Gozal E, Vlasic V, Lasky JA, Liu JY. Brainstem activation of platelet-derived growth factor-beta receptor modulates the late phase of the hypoxic ventilatory response. J Neurochem. 2000;74:310–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

