Genetic determinants of long-term changes in blood lipid concentrations: 10-year follow-up of the GLACIER study
- PMID: 24922540
- PMCID: PMC4055682
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004388
Genetic determinants of long-term changes in blood lipid concentrations: 10-year follow-up of the GLACIER study
Abstract
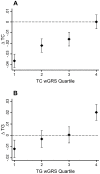
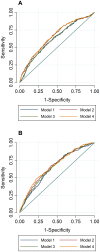
Recent genome-wide meta-analyses identified 157 loci associated with cross-sectional lipid traits. Here we tested whether these loci associate (singly and in trait-specific genetic risk scores [GRS]) with longitudinal changes in total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels in a population-based prospective cohort from Northern Sweden (the GLACIER Study). We sought replication in a southern Swedish cohort (the MDC Study; N = 2,943). GLACIER Study participants (N = 6,064) were genotyped with the MetaboChip array. Up to 3,495 participants had 10-yr follow-up data available in the GLACIER Study. The TC- and TG-specific GRSs were strongly associated with change in lipid levels (β = 0.02 mmol/l per effect allele per decade follow-up, P = 2.0 × 10(-11) for TC; β = 0.02 mmol/l per effect allele per decade follow-up, P = 5.0 × 10(-5) for TG). In individual SNP analysis, one TC locus, apolipoprotein E (APOE) rs4420638 (β = 0.12 mmol/l per effect allele per decade follow-up, P = 2.0 × 10(-5)), and two TG loci, tribbles pseudokinase 1 (TRIB1) rs2954029 (β = 0.09 mmol/l per effect allele per decade follow-up, P = 5.1 × 10(-4)) and apolipoprotein A-I (APOA1) rs6589564 (β = 0.31 mmol/l per effect allele per decade follow-up, P = 1.4 × 10(-8)), remained significantly associated with longitudinal changes for the respective traits after correction for multiple testing. An additional 12 loci were nominally associated with TC or TG changes. In replication analyses, the APOE rs4420638, TRIB1 rs2954029, and APOA1 rs6589564 associations were confirmed (P ≤ 0.001). In summary, trait-specific GRSs are robustly associated with 10-yr changes in lipid levels and three individual SNPs were strongly associated with 10-yr changes in lipid levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Middelberg RP, Martin NG, Whitfield JB (2006) Longitudinal genetic analysis of plasma lipids. Twin Res Hum Genet 9: 550–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

