Impact of comprehensive geriatric assessment on survival, function, and nutritional status in elderly patients with head and neck cancer: protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (EGeSOR)
- PMID: 24923533
- PMCID: PMC4081503
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-427
Impact of comprehensive geriatric assessment on survival, function, and nutritional status in elderly patients with head and neck cancer: protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (EGeSOR)
Abstract
Background: Survival is poorer in elderly patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas [HNSCCs] than in younger patients. Possible explanations include a contribution of co-morbidities to mortality, frequent refusal of standard therapy, and the use of suboptimal treatments due to concern about toxicities. The Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment [CGA] is a multidimensional assessment of general health that can help to customise treatment and follow-up plans. The CGA has been proven effective in several health settings but has not been evaluated in randomised studies of patients with cancer. Our aim here was to assess the impact of the CGA on overall survival, function, and nutritional status of elderly patients with HNSCC.
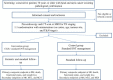
Methods/design: EGeSOR is an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, parallel-group trial in patients aged 70 years or older and receiving standard care for HNSCC. The intervention includes four components: the CGA conducted by a geriatrician before cancer treatment, participation of the same geriatrician in cancer treatment selection, a standardised geriatric therapeutic intervention designed by the same geriatrician; and geriatric follow-up for 24 months. The primary endpoint, assessed after 6 months, is a composite criterion including death, functional impairment [Activities of Daily Living score decrease ≥ 2], and weight loss ≥ 10%. Secondary endpoints include progression-free survival, unscheduled admissions, quality of life, treatment toxicities, costs, and completion of the planned cancer treatment. A centralised online system is used to perform 1:1 randomisation with a minimisation algorithm for centre, age, T and N stages, and tumour site [oral, oropharyngeal, hypopharyngeal, or laryngeal]. The estimated sample size is 704 patients, who are being recruited by 14 centres in 9 French cities.
Discussion: EGeSOR is the first randomised trial of the CGA in elderly cancer patients. We expect the CGA to have direct clinical benefits on the management of elderly patients with HNSCC. If this expectation is fulfilled, the trial may lead to modifications of the management model for elderly patients with cancer.
Trial registration: Trial registration: NCT02025062.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Grenman R, Chevalier D, Gregoire V, Myers E, Rogers S. Treatment of head and neck cancer in the elderly: European Consensus (panel 6) at the EUFOS Congress in Vienna 2007. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267(10):1619–1621. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Bourhis J, Overgaard J, Audry H, Ang KK, Saunders M, Bernier J, Horiot JC, Le Maitre A, Pajak TF, Poulsen MG, O'Sullivan B, Dobrowsky W, Hliniak A, Skladowski K, Hay JH, Pinto LH, Fallai C, Fu KK, Sylvester R, Pignon JP. Meta-Analysis of Radiotherapy in Carcinomas of Head and neck (MARCH) Collaborative Group. Hyperfractionated or accelerated radiotherapy in head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2006;368(9538):843–854. - PubMed
-
- Cojocariu OM, Huguet F, Lefevre M, Perie S. Prognosis and predictive factors in head-and-neck cancers. Bull Cancer. 2009;96(4):369–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials