Modification of rifamycin polyketide backbone leads to improved drug activity against rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 24923585
- PMCID: PMC4110317
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.572636
Modification of rifamycin polyketide backbone leads to improved drug activity against rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
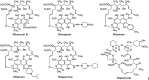
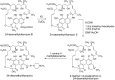
Rifamycin B, a product of Amycolatopsis mediterranei S699, is the precursor of clinically used antibiotics that are effective against tuberculosis, leprosy, and AIDS-related mycobacterial infections. However, prolonged usage of these antibiotics has resulted in the emergence of rifamycin-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. As part of our effort to generate better analogs of rifamycin, we substituted the acyltransferase domain of module 6 of rifamycin polyketide synthase with that of module 2 of rapamycin polyketide synthase. The resulting mutants (rifAT6::rapAT2) of A. mediterranei S699 produced new rifamycin analogs, 24-desmethylrifamycin B and 24-desmethylrifamycin SV, which contained modification in the polyketide backbone. 24-Desmethylrifamycin B was then converted to 24-desmethylrifamycin S, whose structure was confirmed by MS, NMR, and X-ray crystallography. Subsequently, 24-desmethylrifamycin S was converted to 24-desmethylrifampicin, which showed excellent antibacterial activity against several rifampicin-resistant M. tuberculosis strains.
Figures




References
-
- Hartmann G. J., Heinrich P., Kollenda M. C., Skrobranek B., Tropschug M., Weiss W. (1985) Molecular mechanism of action of the antibiotic rifampicin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 24, 1009–1074
-
- Campbell E. A., Korzheva N., Mustaev A., Murakami K., Nair S., Goldfarb A., Darst S. A. (2001) Structural mechanism for rifampicin inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase. Cell 104, 901–912 - PubMed
-
- August P. R., Tang L., Yoon Y. J., Ning S., Müller R., Yu T. W., Taylor M., Hoffmann D., Kim C. G., Zhang X., Hutchinson C. R., Floss H. G. (1998) Biosynthesis of the ansamycin antibiotic rifamycin: deductions from the molecular analysis of the rif biosynthetic gene cluster of Amycolatopsis mediterranei S699. Chem. Biol. 5, 69–79 - PubMed
-
- Schupp T., Toupet C., Engel N., Goff S. (1998) Cloning and sequence analysis of the putative rifamycin polyketide synthase gene cluster from Amycolatopsis mediterranei. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 159, 201–207 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

