Quantification of left ventricular volumes, mass, and ejection fraction using cine displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) MRI
- PMID: 24923710
- PMCID: PMC4311752
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24350
Quantification of left ventricular volumes, mass, and ejection fraction using cine displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To test the hypothesis that magnitude images from cine displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can accurately quantify left ventricular (LV) volumes, mass, and ejection fraction (EF).
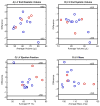
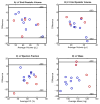
Materials and methods: Thirteen mice (C57BL/6J) were imaged using a 7T ClinScan MRI. A short-axis stack of cine T2-weighted black blood (BB) images was acquired for calculation of LV volumes, mass, and EF using the gold standard sum-of-slices methodology. DENSE images were acquired during the same imaging session in three short-axis (basal, mid, apical) and two long-axis orientations. A custom surface fitting algorithm was applied to epicardial and endocardial borders from the DENSE magnitude images to calculate volumes, mass, and EF. Agreement between the DENSE-derived measures and BB-derived measures was assessed via coefficient of variation (CoV).
Results: 3D surface reconstruction was completed on the order of seconds from segmented images, and required fewer slices to be segmented. Volumes, mass, and EF from DENSE-derived surfaces matched well with BB data (CoVs ≤11%).
Conclusion: LV mass, volumes, and EF in mice can be quantified through sparse (five slices) sampling with DENSE. This consolidation significantly reduces the time required to assess both mass/volume-based measures of cardiac function and advanced cardiac mechanics.
Keywords: DENSE; heart; magnetic resonance imaging; ventricular volume and mass.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Cho GY, Marwick TH, Kim HS, Kim MK, Hong KS, Oh DJ. Global 2-dimensional strain as a new prognosticator in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(7):618–624. - PubMed
-
- Stanton T, Leano R, Marwick TH. Prediction of all-cause mortality from global longitudinal speckle strain: comparison with ejection fraction and wall motion scoring. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009;2(5):356–364. - PubMed
-
- Axel L, Dougherty L. MR imaging of motion with spatial modulation of magnetization. Radiology. 1989;171(3):841–845. - PubMed
-
- Zerhouni EA, Parish DM, Rogers WJ, Yang A, Shapiro EP. Human heart: tagging with MR imaging--a method for noninvasive assessment of myocardial motion. Radiology. 1988;169(1):59–63. - PubMed
-
- Osman NF, Sampath S, Atalar E, Prince JL. Imaging longitudinal cardiac strain on short-axis images using strain-encoded MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2001;46(2):324–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000117/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR033173/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 HL91812-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR033172/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029541/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033173/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD012132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000116/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 1DP5OD012132-01/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL091812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103527/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 8 P20 GM103527-05/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR033171/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

