Targeted iron-oxide nanoparticle for photodynamic therapy and imaging of head and neck cancer
- PMID: 24923902
- PMCID: PMC4155749
- DOI: 10.1021/nn501652j
Targeted iron-oxide nanoparticle for photodynamic therapy and imaging of head and neck cancer
Abstract
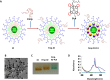
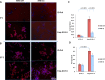
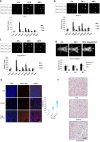
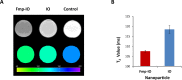
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a highly specific anticancer treatment modality for various cancers, particularly for recurrent cancers that no longer respond to conventional anticancer therapies. PDT has been under development for decades, but light-associated toxicity limits its clinical applications. To reduce the toxicity of PDT, we recently developed a targeted nanoparticle (NP) platform that combines a second-generation PDT drug, Pc 4, with a cancer targeting ligand, and iron oxide (IO) NPs. Carboxyl functionalized IO NPs were first conjugated with a fibronectin-mimetic peptide (Fmp), which binds integrin β1. Then the PDT drug Pc 4 was successfully encapsulated into the ligand-conjugated IO NPs to generate Fmp-IO-Pc 4. Our study indicated that both nontargeted IO-Pc 4 and targeted Fmp-IO-Pc 4 NPs accumulated in xenograft tumors with higher concentrations than nonformulated Pc 4. As expected, both IO-Pc 4 and Fmp-IO-Pc 4 reduced the size of HNSCC xenograft tumors more effectively than free Pc 4. Using a 10-fold lower dose of Pc 4 than that reported in the literature, the targeted Fmp-IO-Pc 4 NPs demonstrated significantly greater inhibition of tumor growth than nontargeted IO-Pc 4 NPs. These results suggest that the delivery of a PDT agent Pc 4 by IO NPs can enhance treatment efficacy and reduce PDT drug dose. The targeted IO-Pc 4 NPs have great potential to serve as both a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) agent and PDT drug in the clinic.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R.; Naishadham D.; Jemal A. Cancer Statistics. Ca—Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. - PubMed
-
- Jermal A.; Bray F.; Center M. M.; Ferlay J.; Forman D. Global Cancer Statistics. Ca—Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Molin Y.; Fayette J. Current Chemotherapies for Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2011, 22, 621–625. - PubMed
-
- Shin D. M.; Khuri F. R. Advances in the Management of Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Head Neck 2013, 35, 443–453. - PubMed
-
- Dolmans D. E.; Fukumura D.; Jain R. K. Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

