Benzylideneacetophenone derivatives attenuate IFN-γ-induced IP-10/CXCL10 production in orbital fibroblasts of patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy through STAT-1 inhibition
- PMID: 24924312
- PMCID: PMC4081550
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2014.26
Benzylideneacetophenone derivatives attenuate IFN-γ-induced IP-10/CXCL10 production in orbital fibroblasts of patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy through STAT-1 inhibition
Abstract
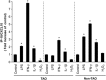
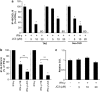
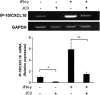
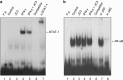
The aim of the present study was to identify a new candidate anti-inflammatory compound for use in the active stage of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). Benzylideneacetophenone compound JC3 [(2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)phenylpro-2-en-l-one] was synthesized based on a structural modification of yakuchinone B, a constituent of the seeds of Alpinia oxyphylla, which belongs to the ginger family (Zingiberaceae), has been widely used in folk medicine as an anti-inflammatory phytochemical. Orbital fibroblasts were primarily cultured from patients with TAO, and the potential of JC3 to suppress the interferon (IFN)-γ-induced protein (IP)-10/CXCL10 production in these cells was determined. IFN-γ strongly increased the level of IP-10/CXCL10 in orbital fibroblasts from patients with TAO. JC3 exerted a significant inhibitory effect on the IFN-γ-induced increase in IP-10/CXCL10 in a dose-dependent manner; its potency was greater than that of an identical concentration of yakuchinone B with no toxicity to cells at the concentration range used. Moreover, the constructed dimer and trimer polystructures of JC3, showed greater potency than JC3 in suppressing the IFN-γ-induced production of IP-10/CXCL10. JC3 significantly attenuated the IP-10/CXCL10 mRNA expression induced by IFN-γ, and a gel-shift assay showed that JC3 suppressed IFN-γ-induced DNA binding of signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT-1) in TAO orbital fibroblasts. Our results provide initial evidence that the JC3 compound reduces the levels of IP-10/CXCL10 protein and mRNA induced by IFN-γ in orbital fibroblasts of TAO patients. Therefore, JC3 might be considered as a future candidate for therapeutic application in TAO that exerts its effects by modulating the pathogenic mechanisms in orbital fibroblasts.
Figures


References
-
- Eckstein AK, Quadbeck B, Tews S, Mann K, Kruger C, Mohr CH, et al. Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: evidence for CD4(+) gammadelta T cells; de novo differentiation of RFD7(+) macrophages, but not of RFD1(+) dendritic cells; and loss of gammadelta and alphabeta T cell receptor expression. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004;88:803–808. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hiromatsu Y, Yang D, Bednarczuk T, Miyake I, Nonaka K, Inoue Y. Cytokine profiles in eye muscle tissue and orbital fat tissue from patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:1194–1199. - PubMed
-
- Wakelkamp IM, Bakker O, Baldeschi L, Wiersinga WM, Prummel MF. TSH-R expression and cytokine profile in orbital tissue of active vs inactive Graves' ophthalmopathy patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2003;58:280–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
