Early release of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) from neurons in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 24924349
- PMCID: PMC4107626
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-106
Early release of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) from neurons in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
Background: Translocation of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) from nucleus could trigger inflammation. Extracellular HMGB1 up-regulates inflammatory response in sepsis as a late mediator. However, little was known about its role in subarachnoid hemorrhage-inducible inflammation, especially in the early stage. This study aims to identify whether HMGB1 translocation occurred early after SAH and also to clarify the potential role of HMGB1 in brain injury following SAH.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into sham group and SAH groups at 2 h, 12 h and on day 1, day 2. SAH groups suffered experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage by injection of 0.3 ml autoblood into the pre-chiasmatic cistern. Rats injected by recombinant HMGB1(rHMGB1) solution were divided into four groups according to different time points. Cultured neurons were assigned into control group and four hemoglobin (Hb) incubated groups. Mixed glial cells were cultured and stimulated in medium from neurons incubated by Hb. HMGB1 expression is measured by western blot analysis, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Downstream nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) subunit P65 and inflammatory factor Interleukin 1β (IL-1β) were measured by western blot and real-time PCR, respectively. Brain injury was evaluated by cleaved caspase-3 staining.
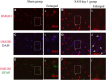
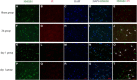
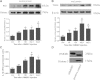
Results: Our results demonstrated HMGB1 translocation occurred as early as 2 h after experimental SAH with mRNA and protein level increased. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence results indicated cytosolic HMGB1 was mainly located in neurons while translocated HMGB1 could also be found in some microglia. After subarachnoid injection of rHMGB1, NF-κB, downstream inflammatory response and cleaved caspase-3 were up-regulated in the cortex compared to the saline control group. In-vitro, after Hb incubation, HMGB1 was also rapidly released from neurons to medium. Incubation with medium from neurons up-regulated IL-1β in mixed glial cells. This effect could be inhibited by HMGB1 specific inhibitor glycyrrhizic acid (GA) treatment.
Conclusion: HMGB1 was released from neurons early after SAH onset and might trigger inflammation as an upstream inflammatory mediator. Extracellular HMGB1 contributed to the brain injury after SAH. These results might have important implications during the administration of specific HMGB1 antagonists early in order to prevent or reduce inflammatory response following SAH.
Figures








References
-
- Schuette AJ, Barrow DL. Epidemiology and long-term mortality in subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2013;80:264–265. - PubMed
-
- Sun Q, Dai Y, Zhang X, Hu YC, Zhang D, Li W, Zhang XS, Zhu JH, Zhou ML, Hang CH. Expression and cell distribution of myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 in the cerebral cortex following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: a pilot study. Brain Res. 2013;1520:134–144. - PubMed
-
- Zhou ML, Shi JX, Hang CH, Zhang FF, Gao J, Yin HX. Expression of Toll-like receptor 4 in the brain in a rabbit experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage model. Inflamm Res. 2007;56:93–97. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Liu DW, Han XY, Dong YN, Gao J, Du B, Meng L, Shi JG. Neuroprotective effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody on apoptosis following subarachnoid hemorrhage in a rat model. J Clin Neurosci. 2012;19:866–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

