Quality of 186 child brain spectra using motion and B0 shim navigated single voxel spectroscopy
- PMID: 24924772
- PMCID: PMC4059781
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24436
Quality of 186 child brain spectra using motion and B0 shim navigated single voxel spectroscopy
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate B0 shim and motion navigated single voxel spectroscopy in children. Assess the repeatability of metabolite concentrations in three regions: medial frontal grey matter, peritrigonal white matter, and basal ganglia. Determine the extent of intra- and interacquisition movement in this population.
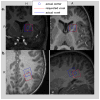
Methods: Linewidth and signal to noise ratio were calculated to assess spectral quality of 186 spectra at 3 Tesla. Repeatability was assessed on 31 repeat scans. Navigator images were used to assess localization errors, while navigator motion and shim logs were used to demonstrate the efficacy of correction needed during the scans.
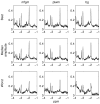
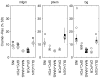
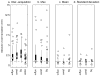
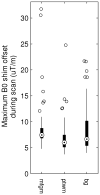
Results: Average linewidths ± standard deviations of N-acetyl aspartate are 3.8 ± 0.6 Hz, 4.4 ± 0.5 Hz, and 4.7 ± 0.8 Hz in each region, respectively. Scan-to-scan measurement variance in metabolite concentrations closely resembled the expected variance. A total of 73% and 32% of children moved before and during the acquisition, causing a voxel shift of more than 10% of the voxel volume, 1.5 mm. The predominant movement directions were sliding out of the coil and nodding (up-down rotation). First-order B0 corrections were significant (>10 μT/m) in 18 % of acquisitions.
Conclusion: Prospective motion and B0 correction provides high quality repeatable spectra. The study found that most children moved between acquisitions and a substantial number moved during acquisitions.
Keywords: B0 correction; motion correction; navigator; single voxel spectroscopy.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Madhi SA, Adrian P, Cotton MF, McIntyre JA, Jean-Philippe P, Meadows S, Nachman S, Käyhty H, Klugman KP, Violari A. Effect of HIV Infection Status and Anti-Retroviral Treatment on Quantitative and Qualitative Antibody Responses to Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Infants. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2010;202:355–361. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

