Renal outcomes in patients with type 1 diabetes and macroalbuminuria
- PMID: 24925722
- PMCID: PMC4178441
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013091004
Renal outcomes in patients with type 1 diabetes and macroalbuminuria
Abstract
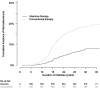
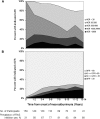
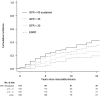
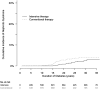
Macroalbuminuria, defined as urine albumin excretion rate (AER)≥300 mg/d, has long been considered a stage of irreversible kidney damage that leads reliably to GFR loss. We examined the long-term renal outcomes of persons with type 1 diabetes who developed incident macroalbuminuria during the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. One hundred fifty-nine participants developed incident macroalbuminuria and were subsequently followed for a median duration of 9 years (maximum of 25 years). At the time of macroalbuminuria diagnosis, mean (SD) age was 37 (9) years, mean (SD) duration of diabetes was 17 (5) years, median AER was 524 mg/d, and mean (SD) eGFR was 108 (20) ml/min per 1.73 m(2). Ten years after macroalbuminuria diagnosis, the cumulative incidence of a sustained reduction in AER to <300 mg/d was 52%, mostly but not entirely under treatment with renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. The cumulative incidence of impaired GFR (sustained eGFR<60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)) 10 years after macroalbuminuria diagnosis was 32%, including 16% who developed ESRD. Lower hemoglobin A1c and BP and regression to AER<300 mg/d were associated with reduced risk of developing impaired GFR. In conclusion, people with type 1 diabetes who develop macroalbuminuria are at high risk of progressive kidney disease. However, through at least 10 years of follow-up, AER could often be controlled, and GFR frequently remained in the normal range.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Are post-trial observational studies useful?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Oct;25(10):2148-50. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014040410. Epub 2014 Jun 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24925718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mogensen CE, Christensen CK, Vittinghus E: The stages in diabetic renal disease. With emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 32[Suppl 2]: 64–78, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Krolewski AS, Warram JH, Christlieb AR, Busick EJ, Kahn CR: The changing natural history of nephropathy in type I diabetes. Am J Med 78: 785–794, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T: Diabetic nephropathy in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: An epidemiological study. Diabetologia 25: 496–501, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Molitch ME, Steffes M, Sun W, Rutledge B, Cleary P, de Boer IH, Zinman B, Lachin J, Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study Group : Development and progression of renal insufficiency with and without albuminuria in adults with type 1 diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial and the epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes Care 33: 1536–1543, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

