Bitterness intensity prediction of berberine hydrochloride using an electronic tongue and a GA-BP neural network
- PMID: 24926369
- PMCID: PMC4043613
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1614
Bitterness intensity prediction of berberine hydrochloride using an electronic tongue and a GA-BP neural network
Abstract
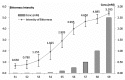
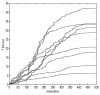
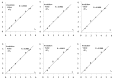
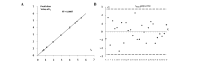
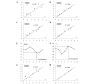
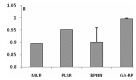
The aim of this study was to predict the bitterness intensity of a drug using an electronic tongue (e-tongue). The model drug of berberine hydrochloride was used to establish a bitterness prediction model (BPM), based on the taste evaluation of bitterness intensity by a taste panel, the data provided by the e-tongue and a genetic algorithm-back-propagation neural network (GA-BP) modeling method. The modeling characteristics of the GA-BP were compared with those of multiple linear regression, partial least square regression and BP methods. The determination coefficient of the BPM was 0.99965±0.00004, the root mean square error of cross-validation was 0.1398±0.0488 and the correlation coefficient of the cross-validation between the true and predicted values was 0.9959±0.0027. The model is superior to the other three models based on these indicators. In conclusion, the model established in this study has a high fitting degree and may be used for the bitterness prediction modeling of berberine hydrochloride of different concentrations. The model also provides a reference for the generation of BPMs of other drugs. Additionally, the algorithm of the study is able to conduct a rapid and accurate quantitative analysis of the data provided by the e-tongue.
Keywords: berberine hydrochloride; bitterness intensity; bitterness prediction model; electronic tongue; genetic algorithm-back-propagation neural network.
Figures


Similar articles
-
One of the major challenges of masking the bitter taste in medications: an overview of quantitative methods for bitterness.Front Chem. 2024 Aug 14;12:1449536. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1449536. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39206439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of bitterness and astringency of green tea with different taste by electronic nose and tongue.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 31;13(12):e0206517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206517. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30596674 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory evaluation of the taste of berberine hydrochloride using an Electronic Tongue.Fitoterapia. 2013 Apr;86:137-43. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Fitoterapia. 2013. PMID: 23481282
-
[Study on superposition law of drug bitterness based on tongue taste evaluation and electronic tongue evaluation].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Dec;44(23):5134-5142. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190916.310. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 32237350 Chinese.
-
[Comprehensive evaluation of palatability for commercial medicine by taste sensing system].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014;134(3):317-23. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00234-3. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 24584008 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Sensitization of Candida albicans to terbinafine by berberine and berberrubine.Biomed Rep. 2016 Apr;4(4):449-452. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.608. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 27073630 Free PMC article.
-
Warfarin maintenance dose Prediction for Patients undergoing heart valve replacement- a hybrid model with genetic algorithm and Back-Propagation neural network.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 26;8(1):9712. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27772-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29946101 Free PMC article.
-
One of the major challenges of masking the bitter taste in medications: an overview of quantitative methods for bitterness.Front Chem. 2024 Aug 14;12:1449536. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1449536. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39206439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A High Sensitivity IDC-Electronic Tongue Using Dielectric/Sensing Membranes with Solvatochromic Dyes.Sensors (Basel). 2016 May 10;16(5):668. doi: 10.3390/s16050668. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27171095 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a variety and quality evaluation method for Amomi fructus using GC, electronic tongue, and electronic nose.Front Chem. 2023 Jun 15;11:1188219. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1188219. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37398979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li L, Naini V, Ahmed SU. Utilization of a modified special-cubic design and an electronic tongue for bitterness masking formulation optimization. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96:2723–2734. - PubMed
-
- Ross CF, Bohlscheid J, Weller K. Influence of visual masking technique on the assessment of 2 red wines by trained and consumer assessors. J Food Sci. 2008;73:S279–S285. - PubMed
-
- Gaudette NJ, Pickering GJ. The efficacy of bitter blockers on health-relevant bitterants. Journal of Functional Foods. 2012;4:177–184.
-
- Xu J, Bovet LL, Zhao K. Taste masking microspheres for orally disintegrating tablets. Int J Pharm. 2008;359:63–69. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz JK, Reo JP, Hendl O, Worthington JH, Petrossian VD. Evaluation of a taste sensor instrument (electronic tongue) for use in formulation development. Int J Pharm. 2009;367:65–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
