Management of diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
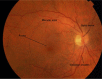
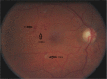
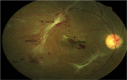
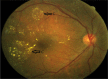
Sub-Saharan Africa faces an epidemic of diabetes. Visual loss from diabetic retinopathy (DR) is both preventable and treatable. This article reviews the epidemiology and clinical features of DR and current evidence-based interventions in three areas: primary prevention of retinopathy by optimum medical management, early detection of pre-symptomatic disease and management of established retinopathy to prevent or mitigate visual loss. There are significant challenges to DR care in resource poor environments. Appropriate provision of effective interventions by health services can reduce social and economic costs associated with patient care.
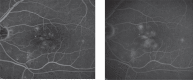
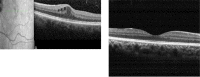
Figures
References
-
- IDF, author. Diabetes atlas. 4th edn. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2009.
-
- Pascolini D, Mariotti SP. Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. BJO. 2012;96(5):614–618. - PubMed
-
- Malawi National STEPS Survey for Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and their Risk Factors. World Health Organisation; 2010. [4th August 2013]. http://www.who.int/chp/steps/Malawi_2009_STEPS_Report.pdf.
-
- Younis N, Broadbent D, Vora J, Harding S. Incidence of sight-threatening retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Liverpool Diabetic Eye Study: a cohort study. Lancet. 2003;361:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BEK, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. III. Prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 or more years. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102:527–532. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
