Frequent coamplification and cooperation between C-MYC and PVT1 oncogenes promote malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 24926545
- PMCID: PMC4287384
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000202
Frequent coamplification and cooperation between C-MYC and PVT1 oncogenes promote malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
Introduction: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a deadly disease with poor prognosis and few treatment options. We characterized and elucidated the roles of C-MYC and PVT1 involved in the pathogenesis of MPM.
Methods: We used small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown in MPM cell lines to determine the effect of C-MYC and PVT1 abrogation on MPM cells undergoing apoptosis, proliferation, and cisplatin sensitivity. We also characterized the expression of microRNAs spanning the PVT1 region in MPM cell lines. Copy number analysis was measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and fluorescence in situ hybridization.
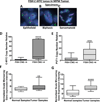
Results: Copy number analysis revealed copy number gains (CNGs) in chromosomal region 8q24 in six of 12 MPM cell lines. MicroRNA analysis showed high miR-1204 expression in MSTO-211H cell lines with four copies or more of PVT1. Knockdown by siRNA showed increased PARP-C levels in MSTO-211H transfected with siPVT1 but not in cells transfected with siC-MYC. C-MYC and PVT1 knockdown reduced cell proliferation and increased sensitivity to cisplatin. Analysis of the expression of apoptosis-related genes in the MSTO-211H cell line suggested that C-MYC maintains a balance between proapoptotic and antiapoptotic gene expression, whereas PVT1 and, to a lesser extent, miR-1204 up-regulate proapoptotic genes and down-regulate antiapoptotic genes. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of MPM tumor specimens showed a high frequency of both CNGs (11 of 75) and trisomy (three copies; 11 of 75) for the C-MYC locus.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that C-MYC and PVT1 CNG promotes a malignant phenotype of MPM, with C-MYC CNG stimulating cell proliferation and PVT1 both stimulating proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Price B. Analysis of current trends in United States mesothelioma incidence. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Larson T, Melnikova N, Davis SI, et al. Incidence and descriptive epidemiology of mesothelioma in the United States, 1999–2002. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2007;13:398–403. - PubMed
-
- Carbone M, Kratzke RA, Testa JR. The pathogenesis of mesothelioma. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:2–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

