B7-H1 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma is associated with sarcomatoid histology and poor prognosis
- PMID: 24926549
- PMCID: PMC4058651
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000177
B7-H1 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma is associated with sarcomatoid histology and poor prognosis
Abstract
Introduction: B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1; aka programmed cell death 1 ligand 1) is a negative costimulatory molecule that is associated with poor prognosis in many tumor types. Given the poor prognosis and the limited treatments available for mesothelioma, we decided to examine B7-H1 expression and its association with survival in patients with mesothelioma.
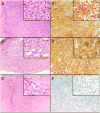
Methods: Expression of B7-H1 was determined in 106 patients using a mouse monoclonal antihuman B7-H1 (clone 5H1-A3) antibody with immunohistochemistry. Positive expression was defined as ≥5% positively stained cells. Clinicopathologic features and survival were compared between B7-H1-positive and B7-H1-negative groups.
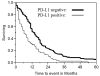
Results: Malignant mesotheliomas of 42 patients (40%) expressed B7-H1. Patients with B7-H1-postive tumors were less likely to be offered or undergo therapeutic surgery (p = 0.03). All sarcomatoid mesotheliomas except one desmoplastic subtype expressed B7-H1. Survival was significantly decreased for patients whose tumors expressed B7-H1 (5 months median, 2-9.5 months interquartile range) compared with those whose tumors did not (14.5 months, 9.25-19 months; p < 0.0001). In a multivariate model, B7-H1 expression and sarcomatoid mesothelioma remained significantly associated with worse survival (risk ratio 1.71, 95% confidence interval 1.03-2.78 [p = 0.04] and risk ratio 2.18, 1.08-4.23 [p = 0.03], respectively).
Conclusions: B7-H1 is expressed in a substantial proportion of malignant pleural mesotheliomas and is associated with poor survival. Almost all malignant pleural mesotheliomas with sarcomatoid differentiation expressed B7-H1. The expression of B7-H1 may have important therapeutic implications for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Figures
References
-
- Stayner L, Welch LS, Lemen R. The worldwide pandemic of asbestos-related diseases. Annu Rev Public Health. 2013;34:205–16. - PubMed
-
- Sterman DH, Recio A, Carroll RG, et al. A phase I clinical trial of single-dose intrapleural IFN-beta gene transfer for malignant pleural mesothelioma and metastatic pleural effusions: high rate of antitumor immune responses. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4456–66. - PubMed
-
- Leigh RA, Webster I. Lymphocytic infiltration of pleural mesothelioma and its significance for survival. S Afr Med J. 1982;61:1007–9. - PubMed
-
- Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, costimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 1999;5:1365–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

