Suicidal behaviour across the African continent: a review of the literature
- PMID: 24927746
- PMCID: PMC4067111
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-606
Suicidal behaviour across the African continent: a review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Suicide is a major cause of premature mortality worldwide, but data on its epidemiology in Africa, the world's second most populous continent, are limited.
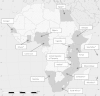
Methods: We systematically reviewed published literature on suicidal behaviour in African countries. We searched PubMed, Web of Knowledge, PsycINFO, African Index Medicus, Eastern Mediterranean Index Medicus and African Journals OnLine and carried out citation searches of key articles. We crudely estimated the incidence of suicide and suicide attempts in Africa based on country-specific data and compared these with published estimates. We also describe common features of suicide and suicide attempts across the studies, including information related to age, sex, methods used and risk factors.
Results: Regional or national suicide incidence data were available for less than one third (16/53) of African countries containing approximately 60% of Africa's population; suicide attempt data were available for <20% of countries (7/53). Crude estimates suggest there are over 34,000 (inter-quartile range 13,141 to 63,757) suicides per year in Africa, with an overall incidence rate of 3.2 per 100,000 population. The recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) estimate of 49,558 deaths is somewhat higher, but falls within the inter-quartile range of our estimate. Suicide rates in men are typically at least three times higher than in women. The most frequently used methods of suicide are hanging and pesticide poisoning. Reported risk factors are similar for suicide and suicide attempts and include interpersonal difficulties, mental and physical health problems, socioeconomic problems and drug and alcohol use/abuse. Qualitative studies are needed to identify additional culturally relevant risk factors and to understand how risk factors may be connected to suicidal behaviour in different socio-cultural contexts.
Conclusions: Our estimate is somewhat lower than GBD, but still clearly indicates suicidal behaviour is an important public health problem in Africa. More regional studies, in both urban and rural areas, are needed to more accurately estimate the burden of suicidal behaviour across the continent. Qualitative studies are required in addition to quantitative studies.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Report 2004. WHO, Geneva 2004.
-
- Public health action for the prevention of suicide. A framework. WHO, Geneva 2012.
-
- Krug EG, Dahlberg TT, Mercy JA, Zwi AB, Lozano R. World report on violence and health. 2002. World Health Organization, Geneva. - PubMed
-
- Wasserman D, Wasserman C. Oxford textbook of suicidology and suicide prevention: a global perspective. 2009. Oxford University Press.
-
- Suicide prevention (SUPRE) [ http://www.who.int/mental_health/prevention/suicide/suicideprevent/en/]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

