Comparison of vilanterol, a novel long-acting beta2 agonist, with placebo and a salmeterol reference arm in asthma uncontrolled by inhaled corticosteroids
- PMID: 24928338
- PMCID: PMC4055937
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5751-13-9
Comparison of vilanterol, a novel long-acting beta2 agonist, with placebo and a salmeterol reference arm in asthma uncontrolled by inhaled corticosteroids
Abstract
Background: Current maintenance therapies for asthma require twice-daily dosing. Vilanterol (VI) is a novel long-acting beta2 agonist, under development in combination with fluticasone furoate, a new inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). Findings from a previous 4-week study suggested that VI has inherent 24-hour activity and is therefore suitable for once-daily dosing. The study described here was a double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, placebo-controlled trial, the aim of which was to assess the efficacy of once-daily VI compared with placebo in patients with persistent asthma. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in 24-hour weighted mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second after 12 weeks of treatment vs. placebo. An active control arm received salmeterol (SAL) twice daily. All patients were maintained on a stable background dose of ICS.
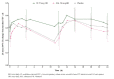
Results: Patients (n = 347) received VI, placebo or SAL (1:1:1). For the primary endpoint, substantial improvements in lung function were seen with VI (359 ml), SAL (283 ml) and placebo (289 ml). There were no statistically significant treatment differences between either the VI (70 ml, P = 0.244) or SAL (-6 ml, P = 0.926) groups and placebo. Both active treatments were well tolerated, with similarly low rates of treatment-related adverse events compared with placebo. No treatment-related serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusions: This study failed to show a treatment difference between VI and placebo for the primary endpoint, in the presence of a placebo response of unforeseen magnitude. Because the placebo response was so large, it is not possible to draw meaningful conclusions from the data. The reason for this magnitude of effect is unclear but it may reflect increased compliance with the anti-inflammatory therapy regimen during the treatment period.
Trial registration: NCT01181895 at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Figures


References
-
- Global initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. http://www.ginasthma.org/local/uploads/files/GINA_Report_2014.pdf.
-
- Reddel HK, Taylor DR, Bateman ED, Boulet LP, Boushey HA, Busse WW, Casale TB, Chanez P, Enright PL, Gibson PG, de Jongste JC, Kerstjens HA, Lazarus SC, Levy ML, O’Byrne PM, Partridge MR, Pavord ID, Sears MR, Sterk PJ, Stoloff SW, Sullivan SD, Szefler SJ, Thomas MD, Wenzel SE. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Task Force on Asthma Control and Exacerbations. An official American thoracic society/European respiratory society statement: asthma control and exacerbations: standardizing endpoints for clinical asthma trials and clinical practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:59–99. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200801-060ST. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

