Induction of vitiligo after imiquimod treatment of condylomata acuminata
- PMID: 24928346
- PMCID: PMC4084792
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-329
Induction of vitiligo after imiquimod treatment of condylomata acuminata
Abstract
Background: Condylomata acuminata (genital warts) is the most common sexually transmitted disease, and imiquimod is the sole FDA-approved medication for combating this condition. Vitiligo associated with imiquimod treatment of condylomata acuminata is rare.
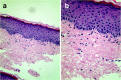
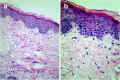
Case presentation: A 28-year-old male with condylomata acuminata of the penis presented to our clinic. After removing his condylomata acuminata, we advised him to use imiquimod 5% cream to prevent relapse. When he presented to our clinic again about 12 weeks later, he complained of vitiligo patches on his penis and scrotum. Physical examination showed vitiligo patches involving the glans penis, shaft of the penis, and scrotum, and remaining pigmented areas within the plaques of vitiligo.A skin biopsy of the dorsal surface of the penis showed a complete absence of melanocytes and melanin granules in the basal layer; the dermis was normal.
Conclusion: This is the first report of a case of imiquimod-induced vitiligo diagnosed by histopathological examination. This adverse effect should be considered when dermatologists prescribe this medication.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

