Effect of non-symmetric waveform on conduction block induced by high-frequency (kHz) biphasic stimulation in unmyelinated axon
- PMID: 24928360
- PMCID: PMC4161638
- DOI: 10.1007/s10827-014-0510-z
Effect of non-symmetric waveform on conduction block induced by high-frequency (kHz) biphasic stimulation in unmyelinated axon
Abstract
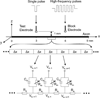
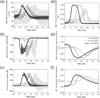
The effect of a non-symmetric waveform on nerve conduction block induced by high-frequency biphasic stimulation is investigated using a lumped circuit model of the unmyelinated axon based on Hodgkin-Huxley equations. The simulation results reveal that the block threshold monotonically increases with the stimulation frequency for the symmetric stimulation waveform. However, a non-monotonic relationship between block threshold and stimulation frequency is observed when the stimulation waveform is non-symmetric. Constant activation of potassium channels by the high-frequency stimulation results in the increase of block threshold with increasing frequency. The non-symmetric waveform with a positive pulse 0.4-0.8 μs longer than the negative pulse blocks axonal conduction by hyperpolarizing the membrane and causes a decrease in block threshold as the frequency increases above 12-16 kHz. On the other hand, the non-symmetric waveform with a negative pulse 0.4-0.8 μs longer than the positive pulse blocks axonal conduction by depolarizing the membrane and causes a decrease in block threshold as the frequency increases above 40-53 kHz. This simulation study is important for understanding the potential mechanisms underlying the nerve block observed in animal studies, and may also help to design new animal experiments to further improve the nerve block method for clinical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Bowman BR, McNeal DR. Response of single alpha motoneurons to high-frequency pulse train: firing behavior and conduction block phenomenon. Applied Neurophysiology. 1986;49:121–138. - PubMed
-
- Boyce WE, Diprima RC. Elementary differential equations and boundary value problems. 6th ed. John Wiley & Sons Inc.; 1997. pp. 436–457.
-
- Camilleri M, Toouli J, Herrera MF, Kow L, Pantoja JP, Billington CJ, Tweden KS, Wilson RR, Moody FG. Selection of electrical algorithms to treat obesity with intermittent vagal block using an implantable medical device. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases. 2009;5:224–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

