Activation of neurotensin receptor type 1 attenuates locomotor activity
- PMID: 24929110
- PMCID: PMC4107019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.05.046
Activation of neurotensin receptor type 1 attenuates locomotor activity
Abstract
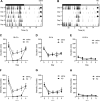
Intracerebroventricular administration of neurotensin (NT) suppresses locomotor activity. However, the brain regions that mediate the locomotor depressant effect of NT and receptor subtype-specific mechanisms involved are unclear. Using a brain-penetrating, selective NT receptor type 1 (NTS1) agonist PD149163, we investigated the effect of systemic and brain region-specific NTS1 activation on locomotor activity. Systemic administration of PD149163 attenuated the locomotor activity of C57BL/6J mice both in a novel environment and in their homecage. However, mice developed tolerance to the hypolocomotor effect of PD149163 (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.). Since NTS1 is known to modulate dopaminergic signaling, we examined whether PD149163 blocks dopamine receptor-mediated hyperactivity. Pretreatment with PD149163 (0.1 or 0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibited D2R agonist bromocriptine (8 mg/kg, i.p.)-mediated hyperactivity. D1R agonist SKF-81297 (8 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced hyperlocomotion was only inhibited by 0.1 mg/kg of PD149163. Since the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) have been implicated in the behavioral effects of NT, we examined whether microinjection of PD149163 into these regions reduces locomotion. Microinjection of PD149163 (2 pmol) into the NAc, but not the mPFC suppressed locomotor activity. In summary, our results indicate that systemic and intra-NAc activation of NTS1 is sufficient to reduce locomotion and NTS1 activation inhibits D2R-mediated hyperactivity. Our study will be helpful to identify pharmacological factors and a possible therapeutic window for NTS1-targeted therapies for movement disorders.
Keywords: D2R; Locomotor activity; NTS1; Neurotensin; Nucleus accumbens; PD149163.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


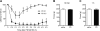


References
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Benfenati F, Battistini N. Neurotensin in vitro markedly reduces the affinity in subcortical limbic 3H-N-propylnorapomorphine binding sites. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983;119:459–461. - PubMed
-
- Binder EB, Kinkead B, Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB. Neurotensin and dopamine interactions. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:453–486. - PubMed
-
- Borroto-Escuela DO, Ravani A, Tarakanov AO, Brito I, Narvaez M, Romero-Fernandez W, Corrales F, Agnati LF, Tanganelli S, Ferraro L, Fuxe K. Dopamine D2 receptor signaling dynamics of dopamine D2-neurotensin 1 receptor heteromers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;435:140–146. - PubMed
-
- Boudin H, Pelaprat D, Rostene W, Beaudet A. Cellular distribution of neurotensin receptors in rat brain: immunohistochemical study using an antipeptide antibody against the cloned high affinity receptor. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:76–89. - PubMed
-
- Boules M, Fredrickson P, Richelson E. Bioactive analogs of neurotensin: focus on CNS effects. Peptides. 2006;27:2523–2533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

