Hypothermia therapy for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in the state of California
- PMID: 24929331
- PMCID: PMC4111956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.04.052
Hypothermia therapy for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in the state of California
Abstract
Objective: To characterize the implementation of hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) in a population-based cohort.
Study design: Using the California Perinatal Quality Care Collaborative and California Perinatal Transport System linked 2010-2012 datasets, we categorized infants≥36 weeks' gestation with HIE as receiving hypothermia or normothermia. Sociodemographic and clinical factors were compared, and multivariable logistic regression was used to determine factors associated with hypothermia therapy.
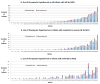
Results: There were 238 reported encephalopathy cases in 2010, 280 in 2011, and 311 in 2012. Hypothermia therapy use in newborns with HIE increased from 59% to 73% across the study period, mainly occurring in newborns with mild or moderate encephalopathy. A total of 36 centers provided hypothermia and cared for 94% of infants, with the remaining 6% being cared for at one of 25 other centers. Of the centers providing hypothermia, 12 centers performed hypothermia therapy to more than 20 patients during the 3-year study period, and 24 centers cared for <20 patients receiving hypothermia. In-hospital mortality was 13%, which primarily was associated with the severity of encephalopathy.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight an opportunity to explore practice-site variation and to develop quality improvement interventions to assure consistent evidence-based care of term infants with HIE and appropriate application of hypothermia therapy for eligible newborns.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Shankaran S. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and novel strategies for neuroprotection. Clinics in perinatology. 2012;39:919–29. - PubMed
-
- Kurinczuk JJ, White-Koning M, Badawi N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early human development. 2010;86:329–38. - PubMed
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1574–84. - PubMed
-
- Simbruner G, Mittal RA, Rohlmann F, Muche R. Systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: outcomes of neo.nEURO.network RCT. Pediatrics. 2010;126:e771–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhou WH, Cheng GQ, Shao XM, Liu XZ, Shan RB, Zhuang DY, et al. Selective head cooling with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial in China. J Pediatr. 2010;157:367–72. 72 e1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

