The glucose transporter Glut1 is selectively essential for CD4 T cell activation and effector function
- PMID: 24930970
- PMCID: PMC4079750
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.05.004
The glucose transporter Glut1 is selectively essential for CD4 T cell activation and effector function
Abstract
CD4 T cell activation leads to proliferation and differentiation into effector (Teff) or regulatory (Treg) cells that mediate or control immunity. While each subset prefers distinct glycolytic or oxidative metabolic programs in vitro, requirements and mechanisms that control T cell glucose uptake and metabolism in vivo are uncertain. Despite expression of multiple glucose transporters, Glut1 deficiency selectively impaired metabolism and function of thymocytes and Teff. Resting T cells were normal until activated, when Glut1 deficiency prevented increased glucose uptake and glycolysis, growth, proliferation, and decreased Teff survival and differentiation. Importantly, Glut1 deficiency decreased Teff expansion and the ability to induce inflammatory disease in vivo. Treg cells, in contrast, were enriched in vivo and appeared functionally unaffected and able to suppress Teff, irrespective of Glut1 expression. These data show a selective in vivo requirement for Glut1 in metabolic reprogramming of CD4 T cell activation and Teff expansion and survival.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

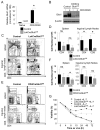
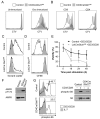

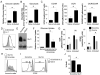

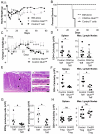
References
-
- Brand S. Crohn’s disease: Th1, Th17 or both? The change of a paradigm: new immunological and genetic insights implicate Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2009;58:1152–1167. - PubMed
-
- Cham CM, Gajewski TF. Glucose availability regulates IFN-gamma production and p70S6 kinase activation in CD8+ effector T cells. J Immunol. 2005;174:4670–4677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI063345/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56AI102074/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI102074/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL108006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138482/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL112311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063345/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL087947/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA138482/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL087947/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007186/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AI106835/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA047741/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD038129/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA047741/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
