CD4-induced activation in a soluble HIV-1 Env trimer
- PMID: 24931470
- PMCID: PMC4231881
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2014.05.001
CD4-induced activation in a soluble HIV-1 Env trimer
Abstract
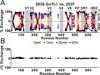
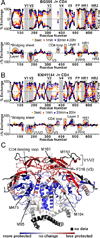
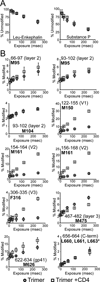
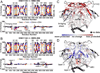
The HIV envelope glycoprotein (Env) trimer undergoes receptor-induced conformational changes that drive fusion of the viral and cellular membranes. Env conformational changes have been observed using low-resolution electron microscopy, but only large-scale rearrangements have been visible. Here, we use hydrogen-deuterium exchange and oxidative labeling to gain a more precise understanding of the unliganded and CD4-bound forms of soluble Env trimers (SOSIP.664), including their glycan composition. CD4 activation induces the reorganization of bridging sheet elements, V1/V2 and V3, much of the gp120 inner domain, and the gp41 fusion subunit. Two CD4 binding site-targeted inhibitors have substantially different effects: NBD-556 partially mimics CD4-induced destabilization of the V1/V2 and V3 crown, whereas BMS-806 only affects regions around the gp120/gp41 interface. The structural information presented here increases our knowledge of CD4- and small molecule-induced conformational changes in Env and the allosteric pathways that lead to membrane fusion.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

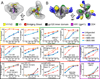
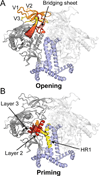
Comment in
-
The HIV-1 Env trimer in HD.Structure. 2014 Jul 8;22(7):935-6. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.06.004. Structure. 2014. PMID: 25007222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binley JM, Sanders RW, Clas B, Schuelke N, Master A, Guo Y, Kajumo F, Anselma DJ, Maddon PJ, Olson WC, Moore JP. A recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein complex stabilized by an intermolecular disulfide bond between the gp120 and gp41 subunits is an antigenic mimic of the trimeric virion-associated structure. J Virol. 2000;74:627–643. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan DC, Fass D, Berger JM, Kim PS. Core structure of gp41 from the HIV envelope glycoprotein. Cell. 1997;89:263–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM099989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI100663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM080352/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37-AI36082/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI41420/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI084817/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084817/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM099989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI084817/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI036082/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41-GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM007750/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AI82362/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 280829/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- F32 GM097805/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00-GM080352/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32-GM097805/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007750/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041420/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI082362/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

