Gene network inference by probabilistic scoring of relationships from a factorized model of interactions
- PMID: 24931990
- PMCID: PMC4229904
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu287
Gene network inference by probabilistic scoring of relationships from a factorized model of interactions
Abstract
Motivation: Epistasis analysis is an essential tool of classical genetics for inferring the order of function of genes in a common pathway. Typically, it considers single and double mutant phenotypes and for a pair of genes observes whether a change in the first gene masks the effects of the mutation in the second gene. Despite the recent emergence of biotechnology techniques that can provide gene interaction data on a large, possibly genomic scale, few methods are available for quantitative epistasis analysis and epistasis-based network reconstruction.
Results: We here propose a conceptually new probabilistic approach to gene network inference from quantitative interaction data. The approach is founded on epistasis analysis. Its features are joint treatment of the mutant phenotype data with a factorized model and probabilistic scoring of pairwise gene relationships that are inferred from the latent gene representation. The resulting gene network is assembled from scored pairwise relationships. In an experimental study, we show that the proposed approach can accurately reconstruct several known pathways and that it surpasses the accuracy of current approaches.
Availability and implementation: Source code is available at http://github.com/biolab/red.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

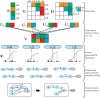
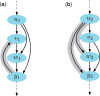

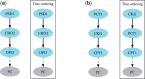

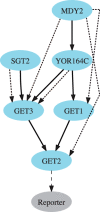
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

