Prevalence of chronic sputum and associated factors in Korean adults
- PMID: 24932085
- PMCID: PMC4055817
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.825
Prevalence of chronic sputum and associated factors in Korean adults
Abstract
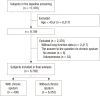
Chronic sputum is a troublesome symptom in many respiratory diseases. The prevalence of chronic sputum varies from 1.2% to 13% according to the country. The purpose of this study was to estimate the prevalence of chronic sputum and to find its associated factors in a general Korean population. We analyzed the data of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010 and 2011. A total number of 6,783 subjects aged 40 yr or more were enrolled in this study with 3,002 men and 3,781 women. As a result, the prevalence of chronic sputum was 6.3% (n=430). Significant risk factors for chronic sputum by multivariate analysis were: age (≥ 70 yr) (odds ratio [OR], 1.954; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.308-2.917), current smoking (OR, 4.496; 95% CI, 3.001-6.734), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (OR, 1.483; 95% CI, 1.090-2.018), and tuberculosis (OR, 1.959; 95% CI, 1.307-2.938). In conclusion, the prevalence of chronic sputum in Korea was in the intermediate range compared with other countries. Smoking is a preventable risk factor identified in this study, and major respiratory diseases, such as COPD and tuberculosis, should be considered in subjects with chronic sputum.
Keywords: Associated Factor; Chronic Sputum; Prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary vitamin C intake protects against COPD: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2012.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Oct 31;11:2721-2728. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S119448. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27843308 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among never-smokers in Korea.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015 Mar 5;10:497-506. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S77662. eCollection 2015. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015. PMID: 25784796 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of obstructive lung disease in a rural setting in the Philippines.Respirology. 2011 Oct;16(7):1111-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02027.x. Respirology. 2011. PMID: 21801277
-
Prevalence of undiagnosed airflow obstruction among people with a history of smoking in a primary care setting.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Sep 27;11:2391-2399. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S106306. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27729780 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of active and passive smoking as risk factors for asthma and COPD in women presenting to primary care in Syria: first report by the WHO-GARD survey group.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2013;8:473-82. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S50551. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2013. PMID: 24124359 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a risk factor for sputum production in the general population: the Nagahama study.Respir Res. 2021 Jan 6;22(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01601-y. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33407482 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Prevalence of Early Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in a Middle-Aged Population: Results from a Nationwide-Representative Sample.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Nov 12;16:3083-3091. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S338118. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 34803377 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of clinical characteristics in patients with Takayasu arteritis with and without concomitant tuberculosis.Heart Vessels. 2016 Aug;31(8):1277-84. doi: 10.1007/s00380-015-0731-8. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Heart Vessels. 2016. PMID: 26266634
References
-
- Vestbo J, Prescott E, Lange P. Association of chronic mucus hypersecretion with FEV1 decline and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease morbidity: Copenhagen City Heart Study Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153:1530–1535. - PubMed
-
- Enright PL, Kronmal RA, Higgins MW, Schenker MB, Haponik EF. Prevalence and correlates of respiratory symptoms and disease in the elderly: Cardiovascular Health Study. Chest. 1994;106:827–834. - PubMed
-
- Anthonisen NR. The British hypothesis revisited. Eur Respir J. 2004;23:657–658. - PubMed
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1256–1276. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:347–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials