Butanol tolerance regulated by a two-component response regulator Slr1037 in photosynthetic Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
- PMID: 24932218
- PMCID: PMC4057619
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-6834-7-89
Butanol tolerance regulated by a two-component response regulator Slr1037 in photosynthetic Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Abstract
Background: Butanol production directly from CO2 in photosynthetic cyanobacteria is restricted by the high toxicity of butanol to the hosts. In previous studies, we have found that a few two-component signal transduction systems (TCSTSs) were differentially regulated in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 after butanol treatment.
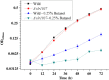
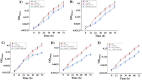
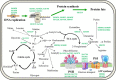
Results: To explore regulatory mechanisms of butanol tolerance, in this work, by constructing gene knockout mutants of the butanol-responsive TCSTS genes and conducting tolerance analysis, we uncovered that an orphan slr1037 gene encoding a novel response regulator was involved in butanol tolerance in Synechocystis. Interestingly, the ∆slr1037 mutant grew similarly to the wild type under several other stress conditions tested, which suggests that its regulation on butanol tolerance is specific. Using a quantitative iTRAQ LC-MS/MS proteomics approach coupled with real-time reverse transcription PCR, we further determined the possible butanol-tolerance regulon regulated by Slr1037. The results showed that, after slr1037 deletion, proteins involved in photosynthesis and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis of central metabolic processes, and glutaredoxin, peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase and glucosylglycerol-phosphate synthase with stress-responsive functions were down-regulated, suggesting that Slr1037 may exhibit regulation to a wide range of cellular functions in combating butanol stress.
Conclusions: The study provided a proteomic description of the putative butanol-tolerance regulon regulated by the slr1037 gene. As the first signal transduction protein identified directly related to butanol tolerance, response regulator Slr1037 could be a natural candidate for transcriptional engineering to improve butanol tolerance in Synechocystis.
Keywords: Butanol; Proteomics; Response regulator; Synechocystis; Tolerance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Co-overexpression of response regulator genes slr1037 and sll0039 improves tolerance of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 to 1-butanol.Bioresour Technol. 2017 Dec;245(Pt B):1476-1483. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.112. Epub 2017 May 4. Bioresour Technol. 2017. PMID: 28533065
-
Elucidating butanol tolerance mediated by a response regulator Sll0039 in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 using a metabolomic approach.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Feb;99(4):1845-57. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6374-y. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25666781
-
Integrated proteomic and metabolomic characterization of a novel two-component response regulator Slr1909 involved in acid tolerance in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.J Proteomics. 2014 Sep 23;109:76-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.06.021. Epub 2014 Jul 3. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24998436
-
An orphan response regulator Sll0649 involved in cadmium tolerance and metal homeostasis in photosynthetic Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.J Proteomics. 2014 May 30;103:87-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.03.029. Epub 2014 Apr 3. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24704854
-
Post-translational Modifications of Serine/Threonine and Histidine Kinases and Their Roles in Signal Transductions in Synechocystis Sp. PCC 6803.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;193(3):687-716. doi: 10.1007/s12010-020-03435-2. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33159456 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic responses to ethanol and butanol in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Oct 17;10:239. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0931-9. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 29075323 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the complete proteome of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Photosynth Res. 2015 Dec;126(2-3):203-19. doi: 10.1007/s11120-015-0140-y. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Photosynth Res. 2015. PMID: 25862646 Review.
-
Systematic and functional identification of small non-coding RNAs associated with exogenous biofuel stress in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Mar 7;10:57. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0743-y. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28286552 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic and systems biology for microbial production of commodity chemicals.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2016 Apr 7;2:16009. doi: 10.1038/npjsba.2016.9. eCollection 2016. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 28725470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic, Genomics, and Responses to Stresses in Cyanobacteria: Biotechnological Implications.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 29;12(4):500. doi: 10.3390/genes12040500. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805386 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Durre P, Fischer RJ, Kuhn A, Lorenz K, Schreiber W, Sturzenhofecker B, Ullmann S, Winzer K, Sauer U. Solventogenic enzymes of Clostridium acetobutylicum: catalytic properties, genetic organization, and transcriptional regulation. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1995;17:251–262. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(95)00006-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

