A rapid nested polymerase chain reaction method to detect circulating cancer cells in breast cancer patients using multiple marker genes
- PMID: 24932314
- PMCID: PMC4049700
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2048
A rapid nested polymerase chain reaction method to detect circulating cancer cells in breast cancer patients using multiple marker genes
Abstract
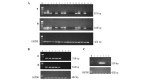
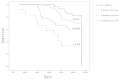
The aim of the present study was to develop a simple and rapid method for the detection of circulating cancer cells using multiple tumor markers and to investigate the clinical significance of circulating cancer cells in breast cancer patients. A novel rapid nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, with high sensitivity and specificity, was evaluated, which was considered to be suitable for clinical application. The rapid nested PCR method was used to detect the circulating cancer cells of 142 breast cancer patients, using a panel of marker genes (FAM83A, NPY1R and KRT19), which were identified by the Digital Gene Expression Displayer Tool of the National Cancer Institute-Cancer Genome Anatomy Project. In total, 79.6% of the 142 breast cancer patient blood samples were found to express at least one tumor marker. In addition, the number of positive markers was found to significantly correlate with the disease stage and presence of distant metastasis. Furthermore, positivity for more than one tumor marker appeared to predict a reduced survival time in breast cancer patients.
Keywords: breast cancer; circulating cancer cells; nested polymerase chain reaction; tumor marker.
Figures

References
-
- Zhao S, Yang H, Zhang M, et al. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) detected by triple-marker EpCAM, CK19, and hMAM RT-PCR and their relation to clinical outcome in metastatic breast cancer patients. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;65:263–273. - PubMed
-
- Reinholz MM, Nibbe A, Jonart LM, et al. Evaluation of a panel of tumor markers for molecular detection of circulating cancer cells in women with suspected breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3722–3732. - PubMed
-
- Margossian A, Diaz J, Corvalan A. In silico analysis of breast cancer transcriptome libraries distinguish tumor subclasses. Cancer Res. 2009;69(Suppl 3):S1165.
-
- Rahbari NN, Bork U, Motschall E, et al. Molecular detection of tumor cells in regional lymph nodes is associated with disease recurrence and poor survival in node-negative colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:60–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
