Tools for diagnosis, monitoring and screening of Schistosoma infections utilizing lateral-flow based assays and upconverting phosphor labels
- PMID: 24932595
- PMCID: PMC4265670
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182014000626
Tools for diagnosis, monitoring and screening of Schistosoma infections utilizing lateral-flow based assays and upconverting phosphor labels
Abstract
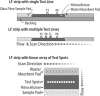
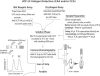
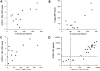
The potential of various quantitative lateral flow (LF) based assays utilizing up-converting phosphor (UCP) reporters for the diagnosis of schistosomiasis is reviewed including recent developments. Active infections are demonstrated by screening for the presence of regurgitated worm antigens (genus specific polysaccharides), whereas anti-Schistosoma antibodies may indicate ongoing as well as past infections. The circulating anodic antigen (CAA) in serum or urine (and potentially also saliva) is identified as the marker that may allow detection of single-worm infections. Quantitation of antigen levels is a reliable method to study effects of drug administration, worm burden and anti-fecundity mechanisms. Moreover, the ratio of CAA and circulating cathodic antigen (CCA) is postulated to facilitate identification of either Schistosoma mansoni or Schistosoma haematobium infections. The UCP-LF assays allow simultaneous detection of multiple targets on a single strip, a valuable feature for antibody detection assays. Although antibody detection in endemic regions is not a useful tool to diagnose active infections, it gains potential when the ratio of different classes of antibody specific for the parasite/disease can be determined. The UCP-LF antibody assay format allows this type of multiplexing, including testing a linear array of up to 20 different targets. Multiple test spots would allow detection of specific antibodies, e.g. against different Schistosoma species or other pathogens as soil-transmitted helminths. Concluding, the different UCP-LF based assays for diagnosis of schistosomiasis provide a collection of tests with relatively low complexity and high sensitivity, covering the full range of diagnostics needed in control programmes for mapping, screening and monitoring.
Figures
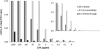
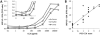
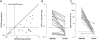

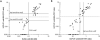
References
-
- Agnew A, Fulford AJC, de Jonge N, Krijger FW, Rodriguezchacon M, Gutsmann V, Deelder AM. The relationship between worm burden and levels of a circulating antigen (CAA) of 5 species of Schistosoma in mice. Parasitology. 1995;111:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Ayele B, Erko B, Legesse M, Hailu A, Medhin G. Evaluation of circulating cathodic antigen (CCA) strip for diagnosis of urinary schistosomiasis in Hassoba school children, Afar, Ethiopia. Parasitex – Journal de la Societe Francaise de Parasitologie. 2008;15:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Bergquist NR. Schistosomiasis research funding – the TDR contribution. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. 1992;87:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Bergquist R, Johansen MV, Utzinger J. Diagnostic dilemmas in helminthology: what tools to use and when? Trends in Parasitology. 2009;25:151–156. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2009.01.004. - PubMed
-
- Bergwerff AA, van Dam GJ, Rotmans JP, Deelder AM, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF. The immunologically reactive part of immunopurified circulating anodic antigen from Schistosoma mansoni is a threonine-linked polysaccharide consisting of → 6)-(beta-D GlcpA-(1 → 3))-beta-D-GalpNAc-(1 → repeating units. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269:31510–31517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

