Key mediators in the immunopathogenesis of allergic asthma
- PMID: 24933589
- PMCID: PMC4253876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.034
Key mediators in the immunopathogenesis of allergic asthma
Abstract
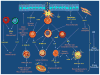
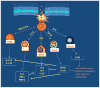
Asthma is described as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the conducting airways. It is characterized by reversible airway obstruction, eosinophil and Th2 infiltration, airway hyper-responsiveness and airway remodeling. Our findings to date have largely been dependent on work done using animal models, which have been instrumental in broadening our understanding of the mechanism of the disease. However, using animals to model a uniquely human disease is not without its drawbacks. This review aims to examine some of the key mediators and cells of allergic asthma learned from animal models and shed some light on emerging mediators in the pathogenesis allergic airway inflammation in acute and chronic asthma.
Keywords: Airway epithelium; Airway hyper-responsiveness; Allergic airway inflammation; Asthma; Innate lymphoid cells; Th17 cells.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Blume C, Davies DE. In vitro and ex vivo models of human asthma. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Jun;84(2):394–400. - PubMed
-
- Hamid Q, Tulic M. Immunobiology of asthma. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:489–507. - PubMed
-
- Ishmael FT. The inflammatory response in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2011 Nov;111(11 Suppl 7):S11–7. - PubMed
-
- Bharadwaj AS, Bewtra AK, Agrawal DK. Dendritic cells in allergic airway inflammation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;85(7):686–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

