Identification of putative pathogenic SNPs implied in schizophrenia-associated miRNAs
- PMID: 24934851
- PMCID: PMC4072616
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-194
Identification of putative pathogenic SNPs implied in schizophrenia-associated miRNAs
Abstract
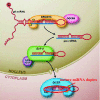
Background: Schizophrenia is a severe brain disorder, and SNPs (Single nucleotide polymorphism) in schizophrenia-associated miRNAs are believed to be one of the important reasons for dysregulation which might contribute to the altered expression of genes and ultimately result in the disease. Identification of causal SNPs in associated miRNAs may have certain significance in understanding the mechanism of schizophrenia.
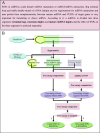
Results: For the above purposes, a method based on detection of free energy change is proposed for identification of causal SNPs in schizophrenia-associated miRNAs. A miRNA is firstly segmented, and free energy change is computed after adding an SNP into a segment. The method discovers successfully 6 out of 32 known SNPs and some artificial SNPs could cause significant change in free energy, and among which, 6 known SNPs are supposed to be responsible for most cases of schizophrenia in population.
Conclusions: The proposed method is not only a convenient way to discover causal SNPs in schizophrenia-associated miRNAs without any biochemical assay or sample comparison between cases and controls, but it also has high resolution for causal SNPs even if the SNPs are not reported for their very rare cases in the population. Moreover, the method can be applied to discover the causal SNPs in miRNAs associated with other diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SNPs in human miRNA genes affect biogenesis and function.RNA. 2009 Sep;15(9):1640-51. doi: 10.1261/rna.1560209. Epub 2009 Jul 17. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19617315 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism associated with mature miR-125a alters the processing of pri-miRNA.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 May 1;16(9):1124-31. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm062. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17400653
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of MicroRNA-related Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Mouse Genome.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 1;10(1):5789. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62588-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32238847 Free PMC article.
-
[Schizophrenia-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms affecting microRNA function].Yi Chuan. 2019 Aug 20;41(8):677-685. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-126. Yi Chuan. 2019. PMID: 31447419 Review. Chinese.
-
Dysregulation of miRNA and its potential therapeutic application in schizophrenia.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Jul;24(7):586-597. doi: 10.1111/cns.12840. Epub 2018 Mar 12. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29529357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two Mutations in the Caprine MTHFR 3'UTR Regulated by MicroRNAs Are Associated with Milk Production Traits.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):e0133015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133015. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26186555 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptive related microRNAs and their role in rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):7265-7272. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05700-3. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32740794 Review.
-
The microRNA cluster miR-183/96/182 contributes to long-term memory in a protein phosphatase 1-dependent manner.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 25;7:12594. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12594. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27558292 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of SNP-triggered miRNA dysregulation in Schizophrenia development.Front Genet. 2024 Jan 26;15:1321232. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1321232. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38343691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An In Vitro Study for the Role of Schizophrenia-Related Potential miRNAs in the Regulation of COMT Gene.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7680-7690. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04070-2. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38427212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barreiro LB, Laval G, Quach H, Patin E, Quintana-Murci L. Natural selection has driven population differentiation in modern humans. Nat Genet. 2008;40:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Kumar V, Westra HJ, Karjalainen J, Zhernakova DV, Esko T, Hrdlickova B, Almeida R, Zhernakova A, Reinmaa E, Vosa U, Hofker MH, Fehrmann RS, Fu J, Withoff S, Metspalu A, Franke L, Wijmenga C. Human disease-associated genetic variation impacts large intergenic non-coding RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003201. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

